When selecting RF connectors, engineers often compare the 2.92mm connector with the SMA connector. While they share similarities in design and compatibility, their performance varies significantly in terms of frequency, durability, and applications. This practical guide will provide a detailed comparison of the 2.92mm connector and the SMA connector, covering their key differences, similarities, and how to select. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge to make an informed and confident purchasing decision.
Overview of 2.92mm and SMA Connector
The 2.92mm and SMA connectors are both precision coaxial connectors widely used in telecommunications, test and measurement, and aerospace and defense industries.
What is a 2.92mm Connector?
The 2.92mm connector, also known as the K connector, is a precision coaxial connector designed for use up to 40 GHz. It was developed as an evolution of the SMA connector to support higher frequency ranges with superior precision. The “2.92mm” name comes from the approximate inner diameter of the outer conductor.
Key features include:
- Threaded coupling mechanism for secure connection.
- Air dielectric with a bead support for low-loss transmission.
- Robust mechanical design for repeated mating.
- Precision machining for minimal reflection and excellent return loss at high frequencies.

Related Posts:
- Unlock High-Frequency Performance: The Ultimate Guide to 2.92mm Connectors
- 5 Common RF High-Frequency Connectors: 1.0mm, 1.85mm, 2.4mm, 2.92mm, and 3.5mm Connectors
What is an SMA Connector?
The SMA (Sub-Miniature version A) connector is one of the most common and widely used RF/microwave connectors in the industry. Developed in the 1960s, it is a semi-precision, sub-miniature connector known for its compact size, durability, and excellent performance for frequencies up to 18 GHz. It features a threaded coupling mechanism and a solid PTFE dielectric, making it a reliable and cost-effective choice for a vast range of applications.
Key characteristics include:
- Threaded coupling with excellent mechanical stability.
- 50-ohm impedance for compatibility across a broad range of RF systems.
- Available in multiple body and plating materials to suit different environments.
- Lower cost compared to precision-grade connectors like 2.92mm.
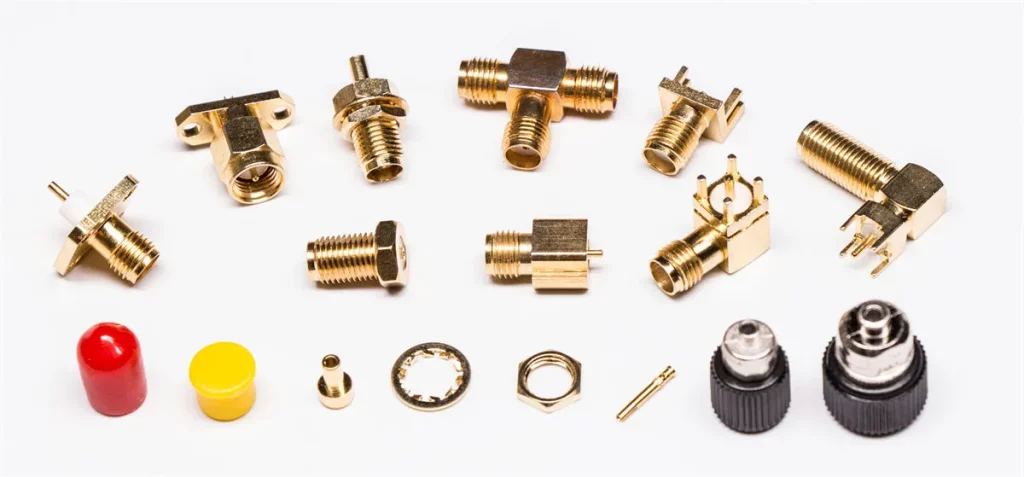

SMA Connectors
Metabee provides various SMA connectors, including
- Female SMA Connectors
- Male SMA Connectors
- SMA Crimp Connectors
- Right Angle SMA Connectors
- PCB Mount SMA Connectors
- Panel Mount SMA Connectors
- Bulkhead SMA Connectors
- Waterproof SMA Connectors
Related Posts:
- What is an SMA Connector? Everything You Need to Know
- SMA Connector Types Explained: Your Essential RF Engineering Guide
Key Differences Between 2.92mm Connector vs. SMA
While 2.92mm and SMA connectors may share a similar outward appearance, their internal design and material choices lead to significant differences in performance, application, and cost. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the right component for your RF system.

Frequency Range
The most critical difference lies in their operational frequency range.
- The 2.92mm connector was designed for high-frequency applications, supporting operation up to 40 GHz with excellent electrical stability.
- Standard SMA connectors are rated up to 18 GHz, with some precision variants extending to 26.5 GHz.
Center Contact Dimensions
The physical design of the center pins differs to ensure performance and prevent damage.
- 2.92mm connectors feature a 2.92mm outer diameter for the inner contact. The male center pin is intentionally shorter than the outer conductor’s contact point. This design can provide tighter mechanical tolerances for high-frequency performance.
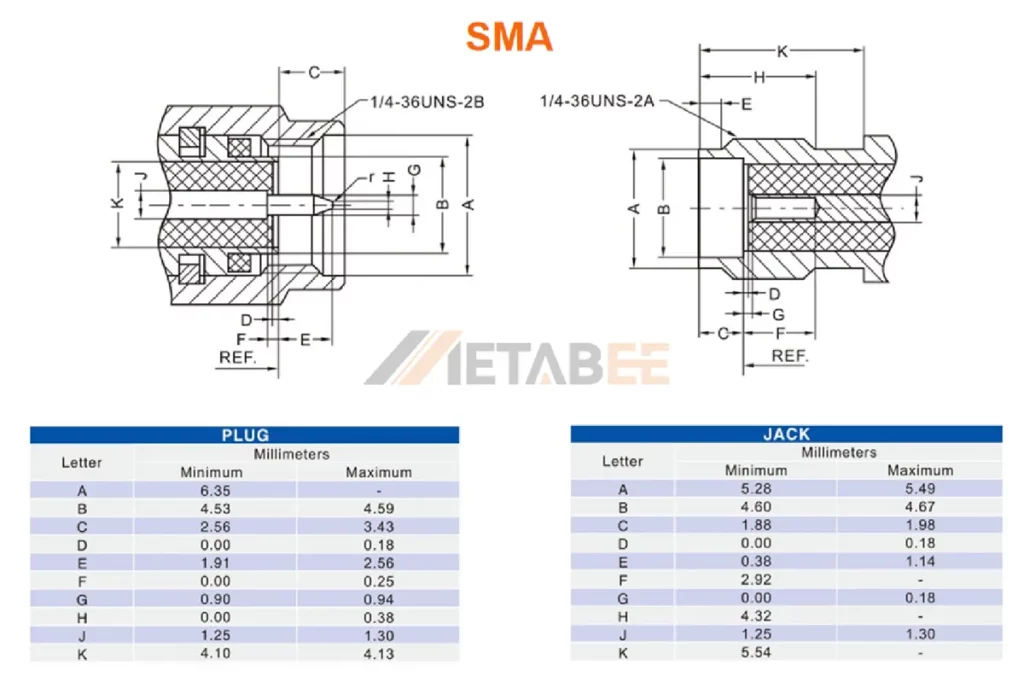
- The male center pin is longer. The standard SMA connector features a 1/4-inch(6.35mm) diameter.
2.92mm Interface Dimensions:
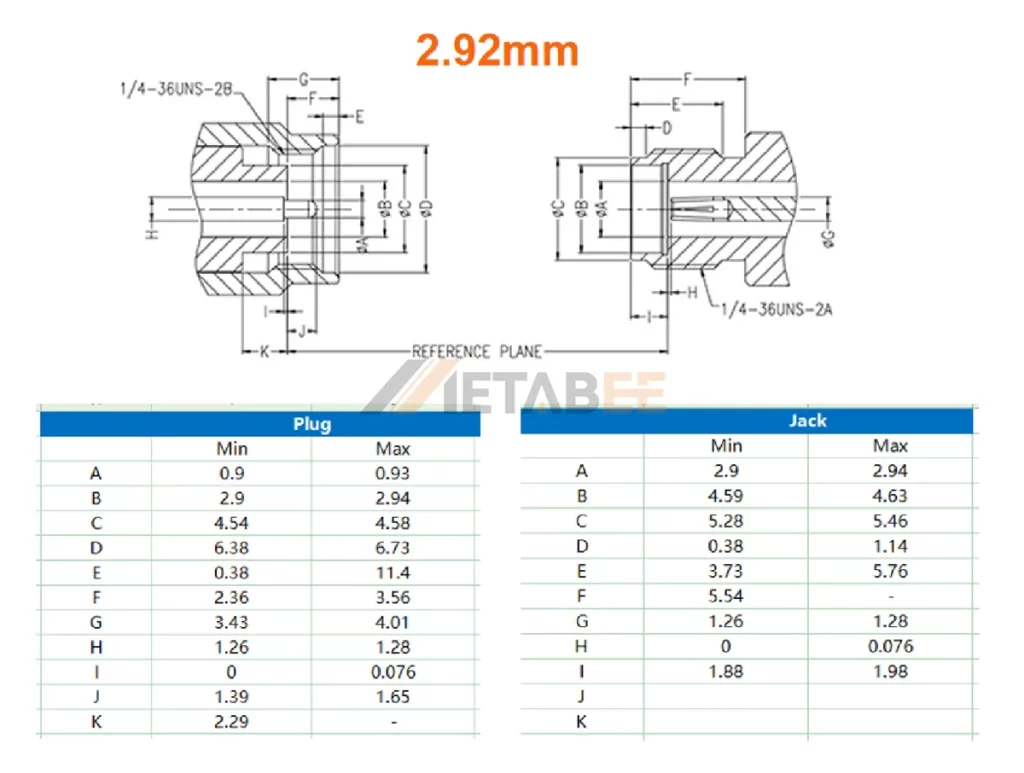
SMA Interface Dimensions:
Shell Material and Plating
The choice of shell material and plating impacts durability, weight, and electrical conductivity.
- 2.92mm connectors: The shells are made from passivated stainless steel or brass with gold plating. These materials ensure optimal electrical performance at high frequencies.
- SMA connectors: The shells are made of copper, often nickel or gold plated for corrosion resistance and improved conductivity.
Contact Material
- The center contacts of 2.92mm connector are always made of beryllium copper plated with gold to ensure excellent electrical conductivity and mechanical spring properties over many mating cycles.
- The center contact of SMA connectors uses phosphor, frequently plated with gold for conductivity and corrosion protection.
Dielectric
The dielectric material’s properties directly influence signal loss and velocity of propagation.
- 2.92mm connector uses an air dielectric with bead support, which reduces dielectric loss at higher frequencies.
- SMA connector uses PTFE(Teflon) dielectric, which is reliable but limits high-frequency performance compared to air dielectrics.
Insertion loss
Insertion loss is the attenuation of signal power as it passes through the connector.
- 2.92mm connectors exhibit lower insertion loss at high frequencies, making them better suited for critical measurement and high-data-rate applications.
- SMA connectors, while adequate for general RF systems, introduce higher loss as frequency increases.
Cost
- The 2.92mm connectors are more expensive due to tighter manufacturing tolerances, precision materials (stainless steel), and the complex air dielectric design.
- The SMA connectors are highly cost-effective and economical due to mass production, less stringent tolerances, and the use of materials.
Application
- 2.92mm connectors: Ideal for high-performance, high-frequency applications. This includes test and measurement equipment, satellite communication systems, 5G development, automotive radar, and high-speed digital component testing.
- SMA connectors: The go-to choice for general-purpose RF and microwave applications up to 18 GHz. Common uses include Wi-Fi and cellular antennas, GPS systems, base stations, and general lab prototyping where cost is a primary consideration.
Summary table for key differences:
| Feature | 2.92mm Connector | SMA Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | DC- 40 Ghz | DC-18 Ghz |
| Center Contact Dimensions | Smaller | Larger |
| Body Material | Stainless Steel | Copper |
| Body Plating | Passivation | Gold or Nickel Plating |
| Contact Material | Beryllium Bronze | Phosphor |
| Dielectric | Air | PTFE (Teflon) |
| Insertion loss | Lower | Higher |
| Cost | More Expensive | More Affordable |
| Applications | Test and Measurement Equipment, Satellite Communication Systems, 5G Development, Automotive Radar. | Wi-Fi, Microwave, Cellular Antennas, GPS Systems, Base Stations. |
Similarities: 2.92mm vs. SMA connector
Despite their differences, they share several fundamental characteristics.
| Feature | 2.92mm Connector | SMA Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Coupling Mechanism | Threaded Coupling | |
| Impedance | 50 Ohm | |
| Contact Plating | Gold Plating | |
| Compatibility | 2.92mm, SMA, and 3.5mm are mechanically compatible with each other | |
| Durability(Mating) | ≧ 500 Cycles | |
| Temperature Range | -65°C to +155°C | |
How to Choose Between 2.92mm and SMA Connector?
Selecting the right coaxial connector is critical for ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of your RF system. The choice between a 2.92mm (often referred to as K-type or SMK) and an SMA connector hinges on your specific technical requirements and operational constraints. Here are some evaluation factors to help you make an informed decision.
Frequency Range
This is your primary consideration. If your system operates above 18 GHz (up to 40 GHz), the 2.92mm connector is the necessary choice. For applications at or below 18 GHz, the SMA is a perfectly suitable and more economical option.
Size
Both are sub-miniature connectors. For high-density, high-frequency applications, the superior signal integrity of the 2.92mm connector is paramount.
Budget
SMA connectors are the economical choice for high-volume and general RF use. 2.92mm connectors are better suited for precision applications where performance outweighs cost.
Durability
If the connector will undergo frequent mating cycles, SMA connectors often provide longer durability in practical use, though high-grade 2.92mm connectors are designed for rugged environments.
Application
The specific application will also help determine the best connector. For high-frequency, high-performance applications like test and measurement equipment or satellite communications, 2.92mm connectors are the better choice. For general-purpose applications like Wi-Fi antennas or cellular devices, SMA connectors are often sufficient.
Conclusion
The 2.92mm connector supports higher frequencies up to 40 GHz with excellent precision, making it ideal for advanced RF and microwave systems. In contrast, the SMA connector offers a lower-cost solution with solid performance up to 18 GHz and is widely used in general RF testing and communication applications. In summary, evaluate your project’s frequency requirements, budget, and desired performance level before making a selection. By understanding the main differences, you can confidently select the connector that ensures the optimal performance and reliability of your system.
Metabee is a famous connector and cable manufacturer from China. It specializes in the design, development, and production of electronic connectors and industrial cables for a wide range of end markets. We provide a full range of both connector types, adapters, and cables.
If you have any other questions, please feel free to contact us; we are online at any time.
Related Products
FAQs
Q1: What is the main difference between a 2.92mm connector and an SMA connector?
A: The primary difference lies in their operational frequency range and mechanical precision.
- SMA connectors are the industry standard for general-purpose RF and microwave applications, typically performing reliably up to 18 GHz.
- In contrast, 2.92mm connectors are a high-precision, millimeter-wave solution engineered to operate up to 40 GHz, making them suitable for more demanding, higher-frequency applications.
Q2: Can I mate a 2.92mm connector with an SMA connector?
A: Yes. but only in one direction. Female 2.92mm connectors are mechanically compatible with male SMA connectors, but caution is advised to avoid wear on SMA connectors at high frequencies.
Q3: How do insertion loss levels compare between the two?
A: 2.92mm connectors generally exhibit lower insertion loss at higher frequencies compared to SMA connectors. This makes them more suitable for precision testing and high-data-rate applications.
Q4: In what situations is an SMA connector the better choice?
A: SMA connectors are the ideal choice for applications operating below 18 GHz. They are more cost-effective, widely available, and offer robust, reliable performance for a vast array of common RF applications, including Wi-Fi antennas, cellular communication devices, GPS systems, and general RF laboratory setups.
Q5: Are the 2.92 mm and SMA connectors both 50-ohm impedance?
A: Yes, both the 2.92mm connector and the SMA connector are designed and manufactured with a nominal characteristic impedance of 50 ohms. This ensures they are compatible with standard RF coaxial cables and equipment.