In the world of high-frequency electronics, precision and reliability are paramount. Among the various components that contribute to seamless signal transmission, connectors play a crucial role. This article delves into the intricacies of 2.92mm connectors, exploring their definition, standards, features, applications, key specifications, interface dimensions, and a comparative analysis with SMA connectors.
What are 2.92mm Connectors?
Definition
2.92mm connectors (also known as K-type, SMK, or SMA-K connectors) are RF/microwave coaxial connectors that operate mode-free up to 40 GHz (ULTEM) or 46 GHz (KAPTON).
There are two designs: a standard design with ULTEM insulator technology, qualified to 40 GHz, and a high-frequency design with KAPTON insulator technology, qualified to 46 GHz. Both provide high electrical performance and are available in multiple configurations.
2.92mm connectors were originally introduced by Mario Maury in 1974 and then reintroduced by Wiltron in 1984 as the K connector. They are suitable for high-frequency applications, particularly within microwave and millimeter-wave systems. Their design prioritizes minimal signal loss and distortion, ensuring optimal electrical performance.

Standard
2.92mm connectors adhere to the IEC 61169-35, MIL-PRF-39012, and MIL-STD-348 standards, making them exceptionally well-suited for high-frequency module and test and measurement applications.
Notably, the 2.92mm interface exhibits compatibility with 3.5mm and SMA connectors, though SMA connectors have limitations in higher frequency ranges.
Main Features
- High-frequency operation: Capable of handling frequencies up to 46 GHz.
- Low VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio): Minimizes signal reflections.
- Low insertion loss: Ensures efficient signal transmission.
- Robust mechanical design: Provides durability and reliability.
Applications
- Test and measurement equipment
- Military and aerospace systems
- Satellite communications
- Radar systems
- Telecommunications
Key Specifications of the 2.92mm Connector
Frequency Range
The 2.92mm connector operates effectively across a broad frequency spectrum, typically extending up to 40 or 46 GHz. This high-frequency capability makes it indispensable in applications demanding superior signal integrity and performance.
- 2.9mm connectors for general use, “ULTEM” technology: DC-40 GHz
- 2.9mm connectors for test laboratory use, “KAPTON” technology: DC-46 GHz
Impedance
Maintaining a consistent impedance of 50 ohms is fundamental to the 2.92mm connector’s design. This standardization guarantees compatibility with a wide array of RF and microwave systems, minimizing signal reflections and ensuring efficient power transfer.
Insertion Loss
The connector’s design prioritizes minimal insertion loss, ensuring that signal attenuation is kept to a minimum.
The insertion loss of 2.92mm connectors is:

- 2.9mm connectors for general use, “ULTEM” technology: < 0.5 dB @ 40 GHz (ULTEM)
- 2.9mm connectors for test laboratory use, “KAPTON” technology: < 0.6 dB @ 46 GHz (KAPTON)
This feature is vital for maintaining signal strength and clarity, particularly in long-distance or high-frequency transmissions.
VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio)
2.92mm connectors have low VSWR values, typically below 1.3:1. They minimize signal reflections and ensure efficient power transfer.
Durability
2.92mm connectors are built to endure repeated mating cycles, reflecting their robust mechanical design. Their mechanical endurance is 500 cycles. This durability ensures long-term reliability and consistent performance, even in demanding operational environments.
Summary
When selecting a 2.92mm connector, it is crucial to make sure that the connector you choose can function within the desired frequency range. Besides, you should make sure the VSWR and insertion loss specifications are at a level that is acceptable for the application the connector will be used for.
Below are comprehensive tables detailing all specifications of the 2.92mm connector:
Electrical Characteristics
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Impedance | 50Ω |
| Frequency Range | ULTEM Technology: DC – 40 GHz KAPTON Technology: DC – 46 GHz |
| V.S.W.R. | < 1.3:1 |
| Insertion Loss | ULTEM Technology: < 0.5 dB KAPTON Technology: < 0.6 dB |
| RF Leakage | – 90 dB max |
| Insulation Resistance | ≥ 5000 MΩ |
| Contact Resistance | ≤ 2 mΩ |
| Voltage Rating | 350 V (RMS) |
| Dielectric Withstanding Voltage | 750 V (RMS) |
Mechanical Characteristics
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Endurance | 500 Matings |
| Force to Engage and Disengage | ≤ 23 N cm (2 in/lbs) |
| Mating Torque | 80 to 115 N cm (7 to 10 in/lbs) |
| Coupling Nut Retention Force | ≤ 272 N (61 lbf) |
| Cable Retention Force | .085”: 135 N (30 lbf) .141”: 270 N (60 lbf) |
| Contact Captivation | 28N (6.3 lbf) |
Environmental Characteristics
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | ULTEM Technology: -65°C to +165°C KAPTON Technology: -65°C to +200°C |
| Thermal Shock | MIL-STD 202, Method 108 |
| High Temperature Test | MIL-STD 202, Method 101, Condition B, 5 % |
| MIL-STD 202, Method 213, Condition I, 100g | MIL STD 202, Method 101, Condition B, 5 % |
| Vibration | MIL-STD 202, Method 106 |
| Shock | MIL STD 202, Method 213, Condition I, 100g |
| Moisture Resistance | MIL STD 202, Method 106 |
Materials and Plating
| Material | Plating | |
|---|---|---|
| Bodies | Stainless Steel | Passivated |
| Center Contacts | Beryllium Copper | Gold Plated |
| Gasket | Silicone Rubber | – |
| Insulators | Ultem (Ultem Technology); Kapton (Kapton Technology) | – |
Interface Dimensions of the 2.92mm Connector
The interface dimensions of 2.92mm connectors are meticulously engineered to ensure precise mating and optimal electrical performance.
The interface is compliant with MIL-PRF-39012 and MIL-STD-348, Figures 323-1 and 323-2. The Inner Diameter (ID) is optimized to achieve the specified VSWR when mated with pins measuring 0.0360/0.0368 inches (0.9144 mm/0.9347 mm) in diameter.
The dimensional drawing of the 2.92mm connector interface is as follows:
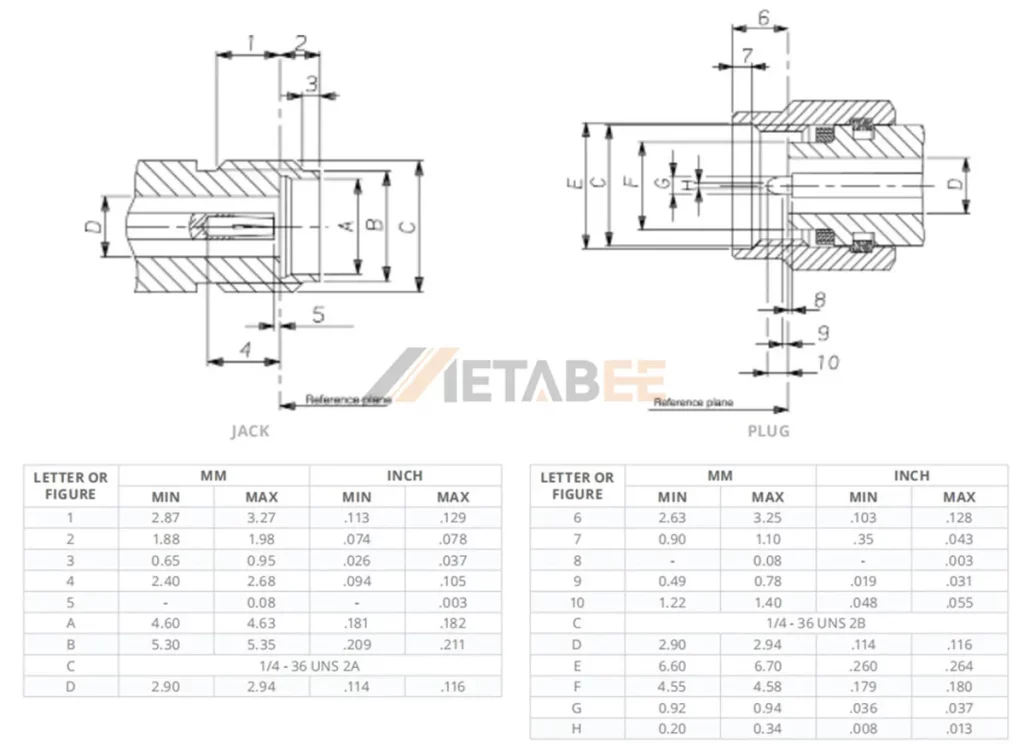
Metabee supplies high-quality 2.92mm connectors that are compliant with all required standards.
2.92mm vs. SMA Connectors
While both 2.92mm and SMA connectors are suitable for high-frequency applications, they differ in their frequency capabilities. SMA connectors typically operate up to 18 GHz, whereas 2.92mm connectors can handle frequencies up to 46 GHz. 2.92mm connectors also offer better VSWR and insertion loss performance at higher frequencies. Therefore, 2.92mm connectors are preferred for applications requiring higher frequency operation and superior performance.
Here’s a clear and concise comparison table between SMA and 2.92mm connectors:
| Parameter | SMA Connector | 2.92mm Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | DC to 18 GHz | DC to 40 GHz (ULTEM), DC to 46 GHz (KAPTON) |
| Impedance | 50 Ω | 50 Ω |
| VSWR (Max) | ≤1.3 (up to 18 GHz) | ≤1.3 (up to 40/46 GHz) |
| Durability | ≥500 mating cycles | ≥500 mating cycles |
| Common Applications | RF modules, consumer electronics | Test equipment, aerospace, mmWave systems |
| Compatibility | Mechanically compatible with 3.5mm and 2.92mm | Mechanically compatible with 3.5mm and SMA |
| Cost | Low | High |
2.92mm connectors are mechanically compatible with SMA connectors. However, it’s important to note that mating a 2.92mm male with an SMA female will result in the performance being limited to the lower frequency capabilities. For optimal performance at higher frequencies, mating 2.92mm with 2.92mm is recommended.

Related Posts:
- What is an SMA Connector? Everything You Need to Know
- SMA Connector Types Explained: Your Essential RF Engineering Guide
Related Products:

Conclusion
2.92mm connectors are essential components in high-frequency systems, offering excellent electrical performance and reliability. Their ability to operate at high frequencies, coupled with low VSWR and insertion loss, makes them ideal for demanding applications. When high-frequency performance is a must, the 2.92mm connector is the ideal choice.
Pingback: 2.92mm vs. SMA Connector: The Practical Guide Before You Buy - MetabeeAI