RF connectors are essential components in electronic systems that join different parts of a circuit or equipment. They come in different shapes, sizes, and types, each designed for specific applications. N-type and UHF connectors are two of the most popular connectors used in RF and microwave applications. This article will explore the comparison of N-type vs. UHF connectors, covering their impedance, frequency range, durability, cost, and applications. Additionally, we will provide a guide to selecting the optimal RF connector for your application.
Overview of UHF Connector and N-type Connector
Before diving into the comparison of N-type vs. UHF connectors, let’s briefly introduce the two connectors.
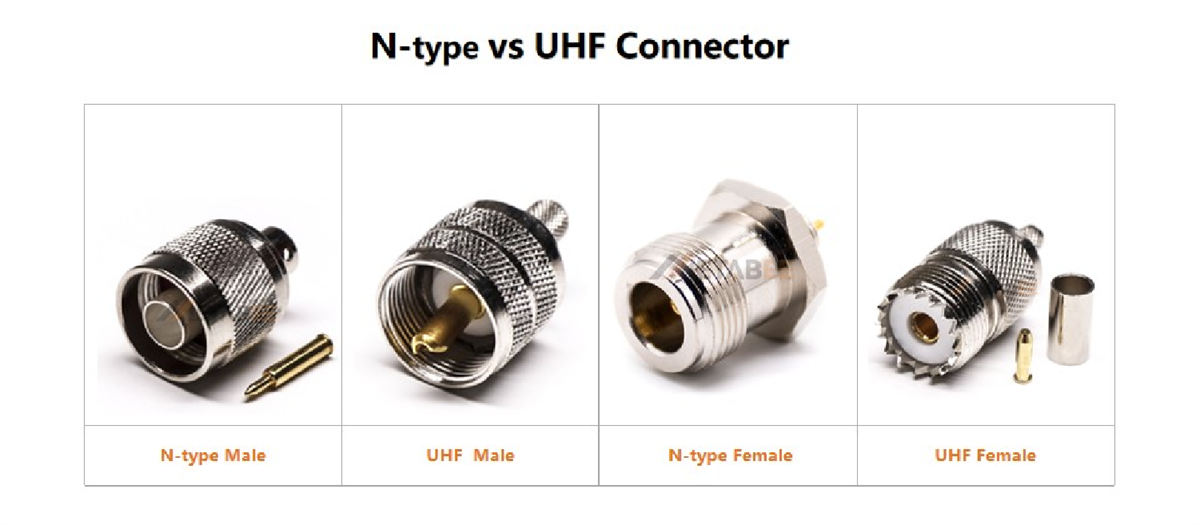
N-type Connector
The N-type connector was developed by Paul Neill at Bell Labs in the 1940s. Its primary purpose was to provide a robust, weatherproof, and relatively high-frequency connector for military radar systems.
Key features and characteristics:
- Threaded coupling mechanism
- 50 Ohm impedance
- Higher frequency range (DC to 11 GHz )
- Robust and weatherproof construction
- Medium-sized
- More robust and stable connection
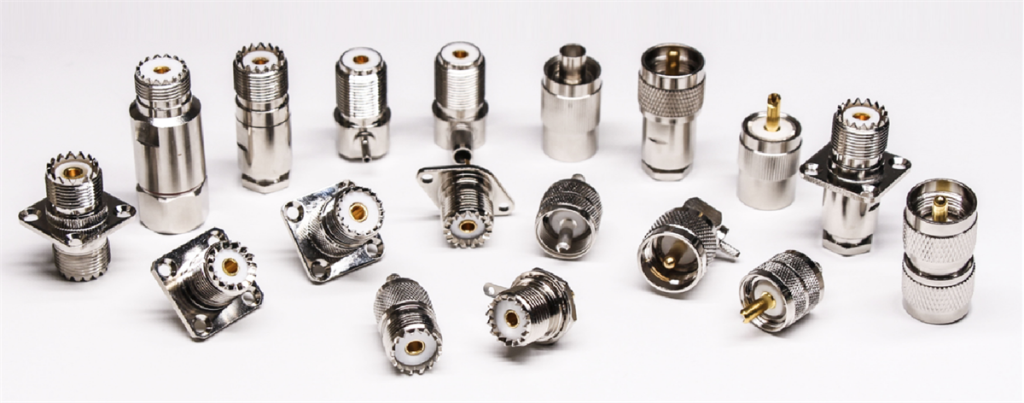
Metabee provides various N-type connectors, including
- Male N-type Connectors
- Female N-Type Connectors
- Panel Mount N-type Connectors
- Right Angle N-type Connectors

UHF Connector (PL-259/SO-239)
UHF connectors are an older design, originating before World War II. Despite its name suggesting “Ultra High Frequency,” the UHF connector was originally designed for use at lower frequencies, primarily High-Frequency (HF) ranges (below 30 MHz).
Key features and characteristics:
- Threaded screw-on coupling (similar to N-type but less precise).
- Non-constant impedance design
- Lower effective frequency range (DC–300 MHz)
- Not-weatherproof
- Performance limitations
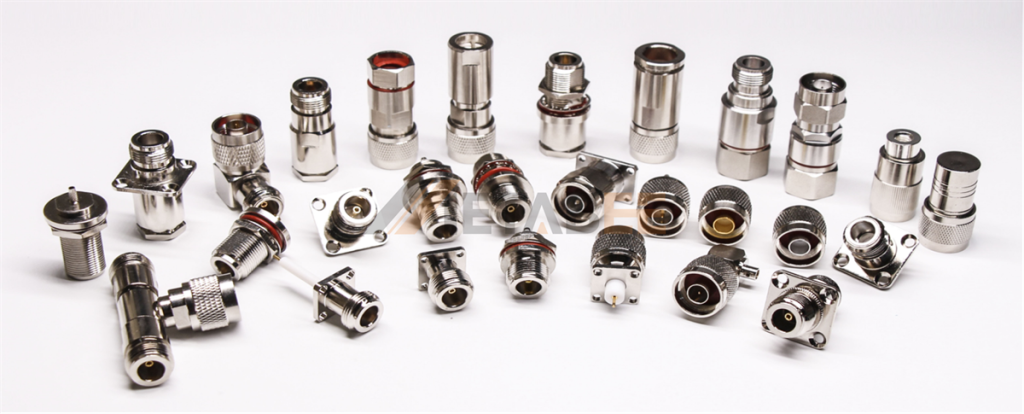
Metabee offers a series of UHF connectors, including
- SO-239/UHF Female Connectors
- PL-259/UHF Male Connectors
- Right Angle UHF Connectors

N-type vs. UHF (PL-259/SO-239) Connectors: 7 Key Differences
The fundamental differences between N-type and UHF connectors lie in their electrical performance, physical characteristics, and design intent.
Impedance
N-type coaxial connectors are precision 50-ohm impedance connectors. This constant impedance is critical for minimizing reflections and ensuring efficient power transfer at high frequencies.
UHF connectors are non-constant impedance connectors. While often used in 50-ohm systems, the impedance of the connector itself is typically around 30-40 ohms. This impedance discontinuity causes reflections, which become more significant as frequency increases, leading to higher VSWR and signal loss.
Frequency Range
N-type RF connectors are rated for reliable performance up to 11 GHz; they are suitable for microwaves and many modern wireless communication bands.
The frequency range of UHF connectors is DC – 300 MHz. Due to their non-constant impedance, they are generally considered optimal below 30 MHz, though they are often used with degraded performance up to 150-300 MHz.
Size and Form Factor
The UHF connector is larger and bulkier, making it less ideal for tight spaces. The UHF and N-type connector thread sizes are both 5/8-24 threaded. N connectors are more compact and mechanically stable for high-vibration environments.
Applications
There is a big difference in the key applications of the N-type vs. the UHF connector.
Applications of N-type connectors
The N-type connectors are preferred for applications requiring precise impedance matching, high-frequency performance, and environmental robustness. Here are some common applications:
- Antennas
- Base Stations
- Instrumentation
- Satellite Systems
- Radar Systems
- Surge Protection
- Professional Broadcast Equipment
Applications of UHF connectors
UHF connectors are suitable for applications where cost is a major factor, frequencies are lower, and precise impedance matching is less critical or compensated for in the system design. Here are some common applications:
- HF Amateur Radio
- CB Radio
- Military
- Legacy Broadcast
- Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS)
- Public Address Systems
- Low-Frequency Applications

Weatherproof
N-type connectors have internal gaskets and a secure threaded coupling, and they are a sealed design and weatherproof. UHF connectors are non-weatherproof, so they need additional sealing for outdoor installations.
Temperature Range
The N-type connectors have a wider operating temperature range, often specified from -55℃to +155℃ for harsh outdoor conditions.
The specific range of UHF connectors can vary depending on the insulator materials used by the manufacturer. PTFE insulators for -65℃ to 165℃; mica-filled phenolic insulators for -55℃ to +149℃; copolymer of styrene and polystyrene for -55℃ to +85℃.
Cost
Due to their more complex design, higher precision manufacturing requirements, and performance capabilities, N-type connectors are generally more expensive than UHF connectors.
Simpler construction and less stringent performance requirements make UHF connectors significantly more affordable to produce and purchase.
Below is a breakdown of a detailed comparison of N-type vs. UHF (PL-259/SO-239) connectors
Key Differences
| Feature | N-type Connectors | UHF Connectors |
|---|---|---|
| Impedance | 50 Ohm | Non-constant |
| Frequency Range | DC–11 GHz | DC–300 MHz |
| Size and Form Factor | More compact | Larger |
| Weatherproof | Weatherproof | Non-weatherproof |
| Temperature Range | -55℃to +155℃ | -65℃ to 165℃ (PTFE) -55℃ to +149℃ -55℃ to +85℃ |
| Cost | More expensive | More affordable |
| Applications | Antennas, Base Stations, Instrumentation, Satellite Systems, Radar Systems, Surge Protection, Professional Broadcast Equipment. | HF Amateur Radio, CB Radio, Military, Legacy Broadcast, Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS), Public Address Systems, Low-Frequency Applications. |
Similarities
| Feature | N-type Connectors | UHF Connectors |
|---|---|---|
| Coupling Mechanism | Threaded Coupling | |
| Fastening Type | 5/8-24 UNEF Thread | |
| Body Material | Brass | |
| Body Plating | Nickel-Plating | |
| Contact Material | Brass | |
| Contact Plating | Gold-Plating | |
| Insulator Material | Teflon | |
| Insulation Resistance | ≧ 5000 MΩ (Megohms MIN . ) | |
| Mating Durability | ≧ 500 Cycles | |
Other Common RF Connector Types and Accessories
Metabee provides some common RF connector types and accessories, including
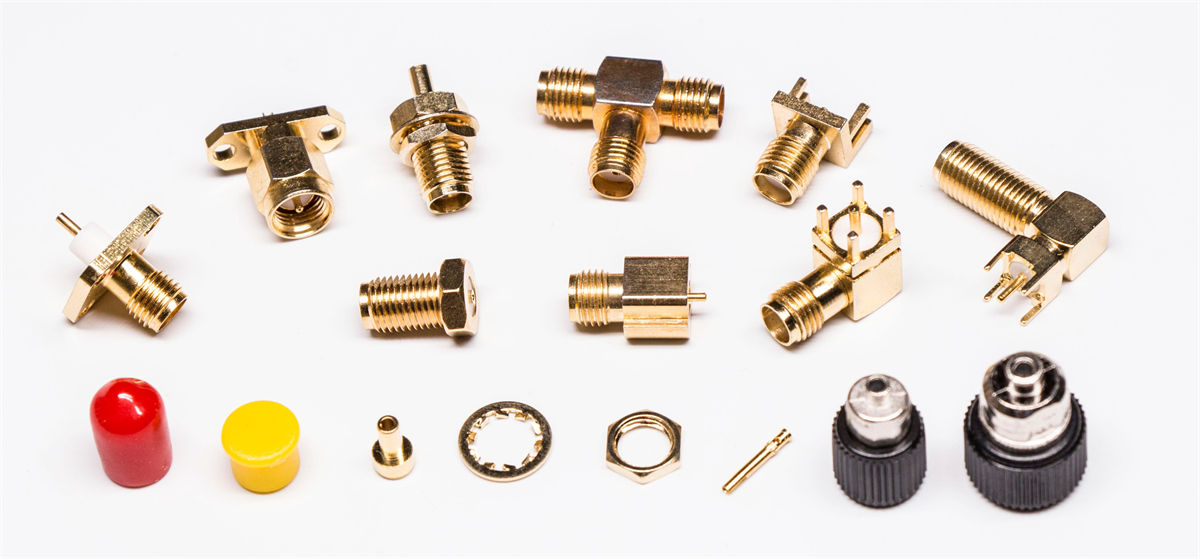
SMA Connectors
SMA (SubMiniature version A) connectors are compact, precision connectors commonly used for microwave frequencies up to 18 GHz and beyond.

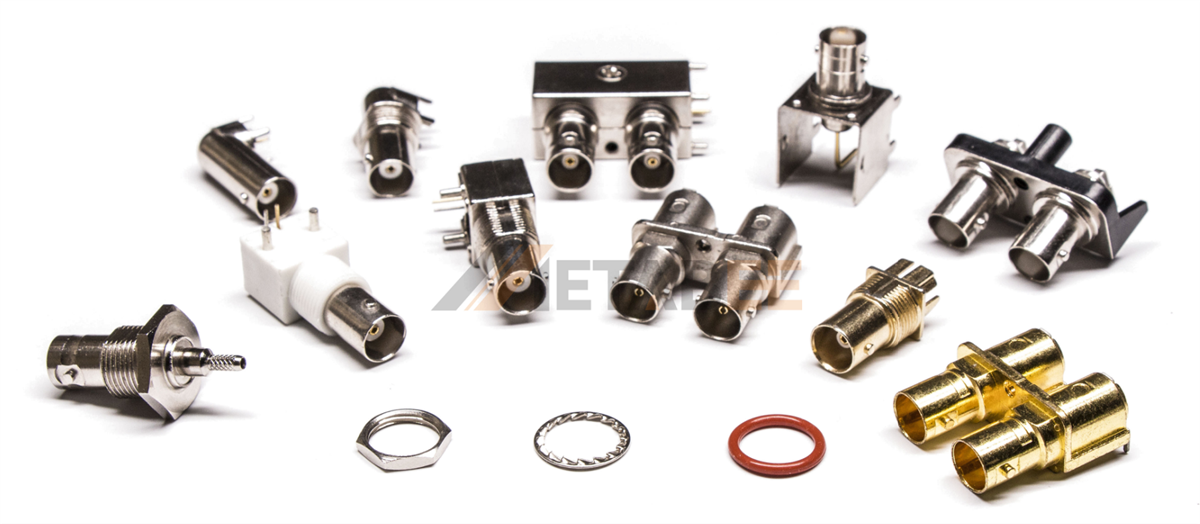
BNC Connectors
BNC (Bayonet Neill-Concelman) connectors are quick-connect/disconnect RF connectors typically used for low-frequency signals up to 4 GHz. They are popular in radio, television, and test instrumentation due to their simple bayonet locking mechanism and ease of use.

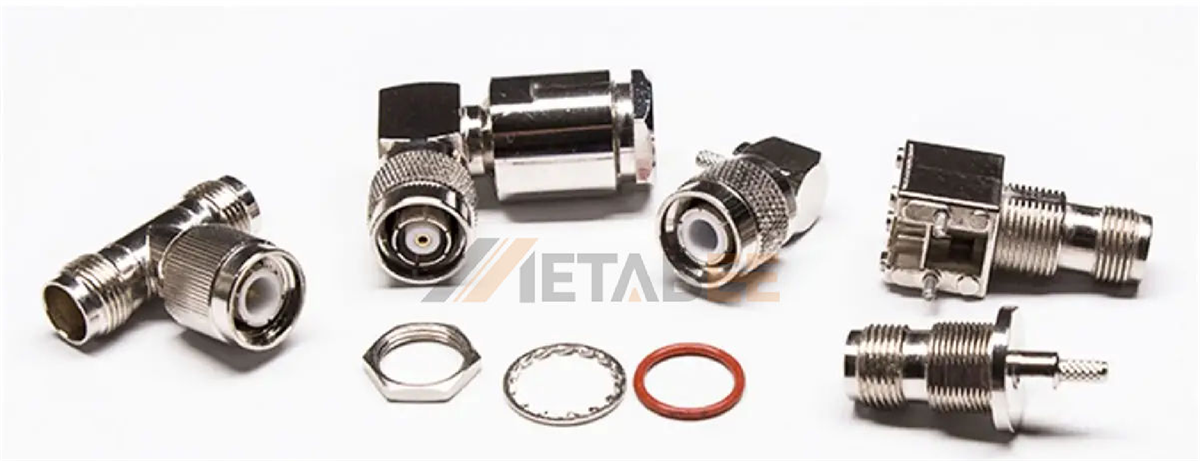
TNC Connectors
TNC (Threaded Neill–Concelman) connectors are a threaded version of the BNC connector, providing better performance at microwave frequencies (up to 11 GHz).

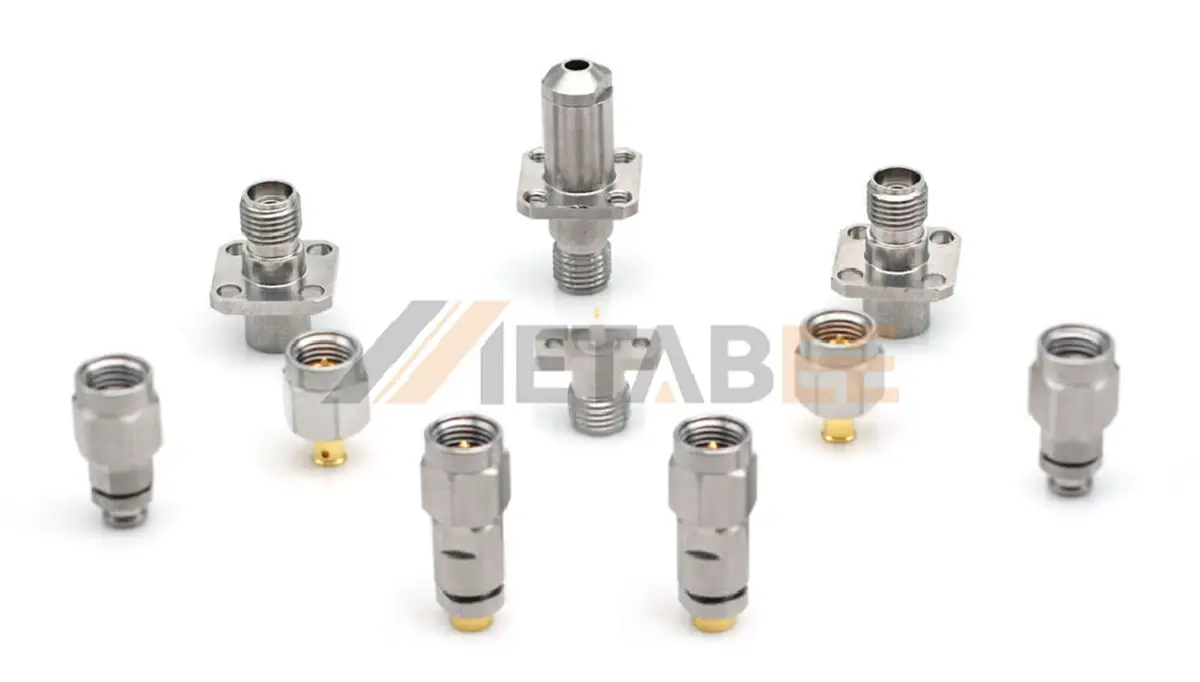
2.92mm Connectors
2.92mm connectors, sometimes called K-connectors, are precision connectors capable of operating up to 40 GHz. They are designed for high-frequency, high-reliability applications.

SMB Connectors
SMB (SubMiniature version B) connectors are smaller than SMA connectors and are suitable for applications requiring quick connect/disconnect capability. They operate effectively up to 4 GHz and are used in automotive, communications, and consumer electronics.
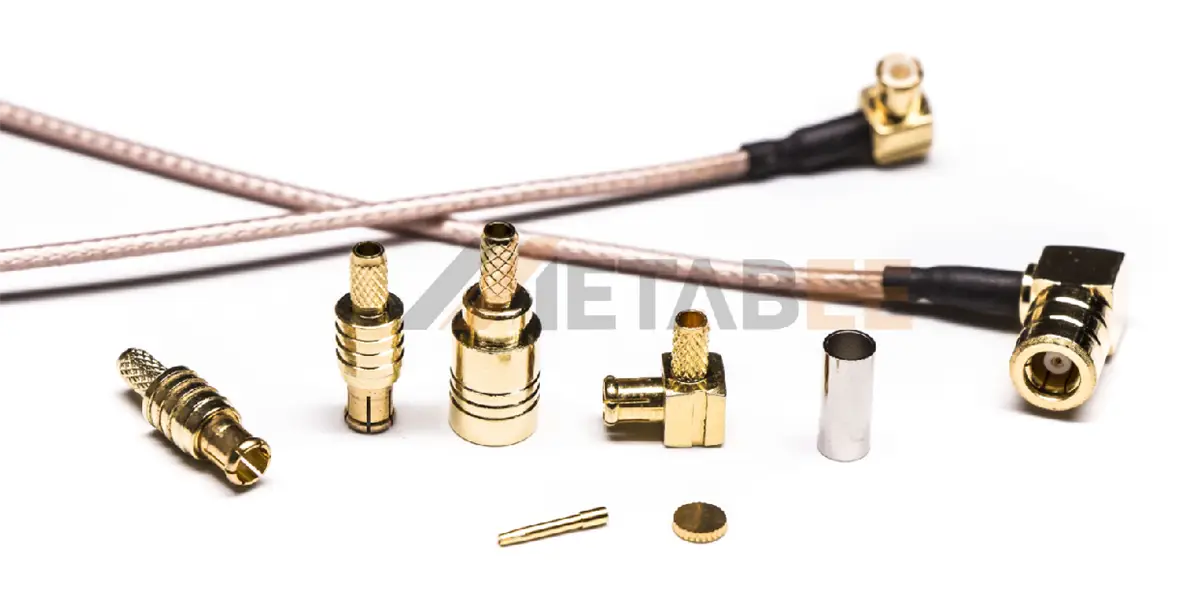

MCX Connectors
MCX connectors offer even smaller form factors than SMB connectors while maintaining performance up to 6 GHz.
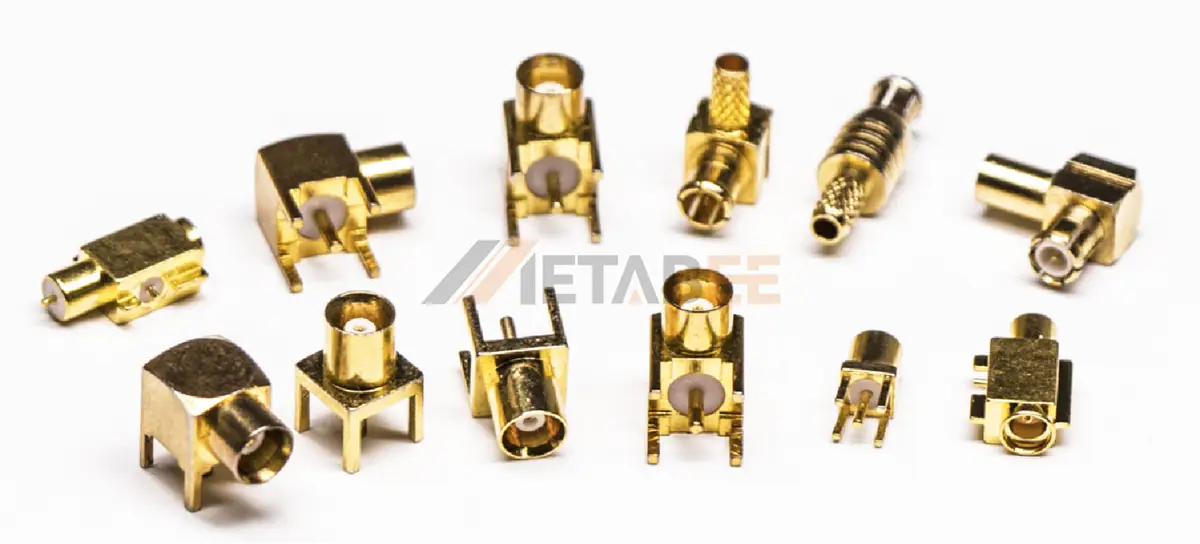

N-type Adapters
N-type adapters are rugged, weatherproof adapters designed for medium- to high-power RF applications.
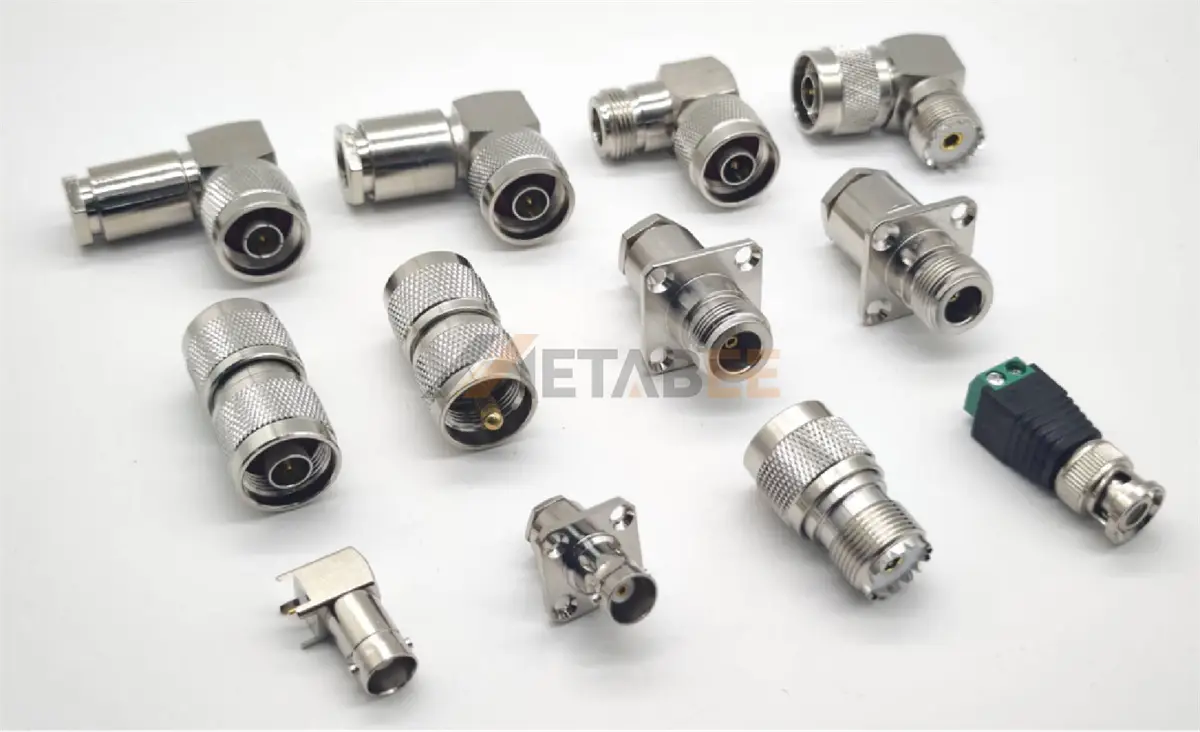

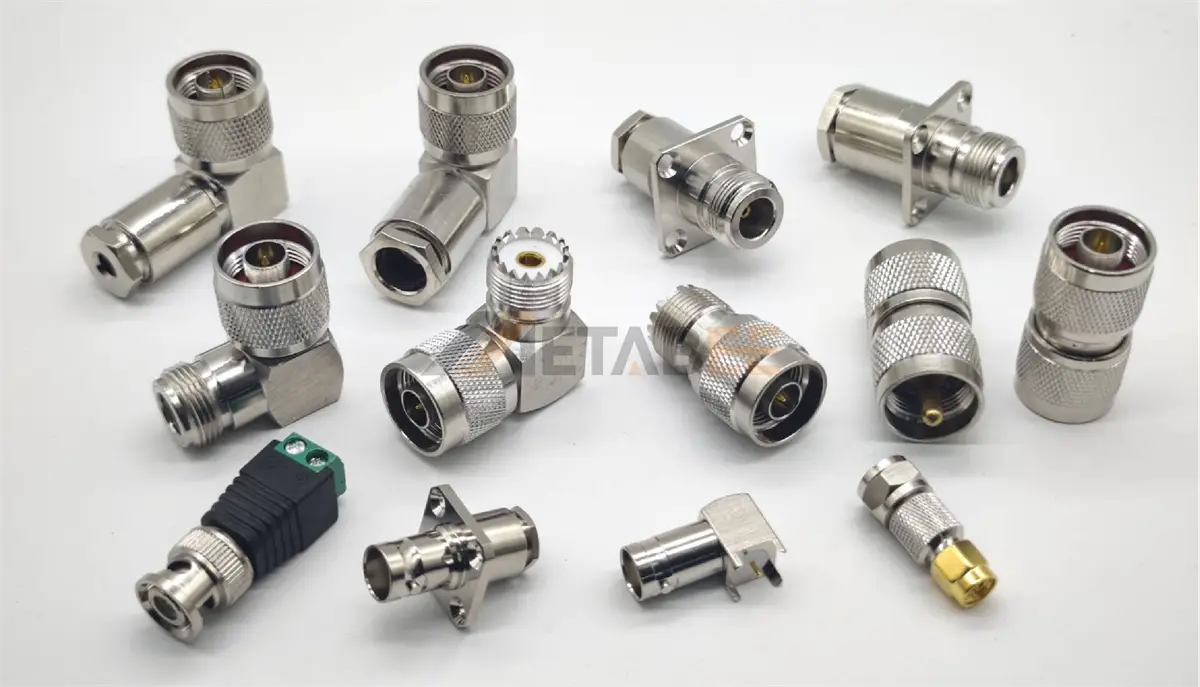
UHF Adapters
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) adapters are typically used for frequencies below 300 MHz. Known for their large size and robust construction, they are common in amateur radio, CB radio, and low-frequency transmission systems.

How to Choose the Right RF Connector
Selecting the optimal RF connector is a critical step in designing, installing, or maintaining any radio frequency system. This guide helps you identify the key factors for choosing the right connector to match your specific needs.
Key Factors in RF Connector Selection:
- Coupling Mechanism
- Connector Type
- Impedance
- Frequency Range
- Connector Size and Form Factor
- Durability and Environmental Factors
- Cost and Budget
Conclusion
This article provides a detailed comparison between N-type and UHF RF connectors. We detail the characteristics of two connectors first. Then we dive into key differences, focusing on critical aspects like impedance matching, superior frequency range of N-connectors, weatherproofing capabilities, size, and cost implications. Next, while noting similarities in materials and basic coupling, it emphasizes how these distinctions impact performance and application suitability. What’s more, the final part also guides you in selecting the optimal RF connector by evaluating factors such as required frequency, impedance, environmental resilience, and budget constraints for their specific RF system needs.
Metabee can provide a comprehensive selection of RF connectors. And we have a professional technical team with high-quality solutions to meet your diverse RF connectivity needs, ensuring superior performance and long-term reliability.
If you have any questions about RF connectors, please contact us, and we will provide powerful help.