Look at the back of your computer, printer, or even an older television. You will often see a D-shaped port with two thumbscrews. This is a D-subminiature, or a D-sub connector. For many years, it was a standard for connecting peripherals. You likely used one to connect your monitor with a VGA cable. Game controllers and network devices also frequently use this reliable connection.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about D-sub connectors. We’ll look at their history, explain the different types, and help you pick the right one for your project.
What is a D-Sub Connector?
Definition
A D-sub connector is a type of electrical connector characterized by its D-shaped metal shell. This shell serves a dual purpose. It provides mechanical support and ensures correct orientation during mating, preventing accidental reversal. Additionally, the distinctive D-shape design offers effective shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI).
Two or more parallel rows of pins and sockets sit inside the shell. And these contacts are typically used to transmit data, power, or signals between devices. The number of contacts can vary widely, from 9 to 104, making these connectors adaptable for a wide range of applications.

History
Early 1950s: The ITT Cannon company developed the first D-Sub connector and patented it in 1952. Designers created the original design to offer a smaller and more efficient solution for connecting electronic equipment. It quickly gained popularity due to its robust design and reliable performance.
1980s-1990s: The D-Sub connector became ubiquitous in the personal computer industry. People use the DB9 for serial ports, the DB25 for parallel printer ports, and the DA15 for VGA monitors.
Modern era: Many of these applications have been replaced by modern standards like USB and DBMI. But the D-Sub connector continues to thrive in specialized and industrial settings where its durability and proven design are indispensable.
Advantages
D-Sub connectors offer several distinct advantages:
- Durability: The robust metal shell and strong contacts make D-Sub connectors highly durable. They work well in harsh industrial environments.
- Cost-Effectiveness: A simple, proven design makes these connectors a very affordable and economical solution.
- EMI/RFI Shielding: The metal shell provides excellent protection against electromagnetic and radio-frequency interference. And this is crucial for sensitive signals.
- Wide Availability: As a long-established standard, they are easy to source globally from many manufacturers.
- Robustness: The metal shell and screw locks provide excellent mechanical stability and resistance to vibration.
Standards
IEC 60603: This international standard defines the general requirements for D-Sub connectors, including dimensions, electrical properties, and safety.
MIL-DTL-24308: This U.S. military standard specifies the rigorous requirements for performance, durability, and environmental resistance in demanding applications.
DIN 41652: This European standard defines the mechanical dimensions and characteristics of D-Sub connectors. It ensures compatibility across manufacturers.
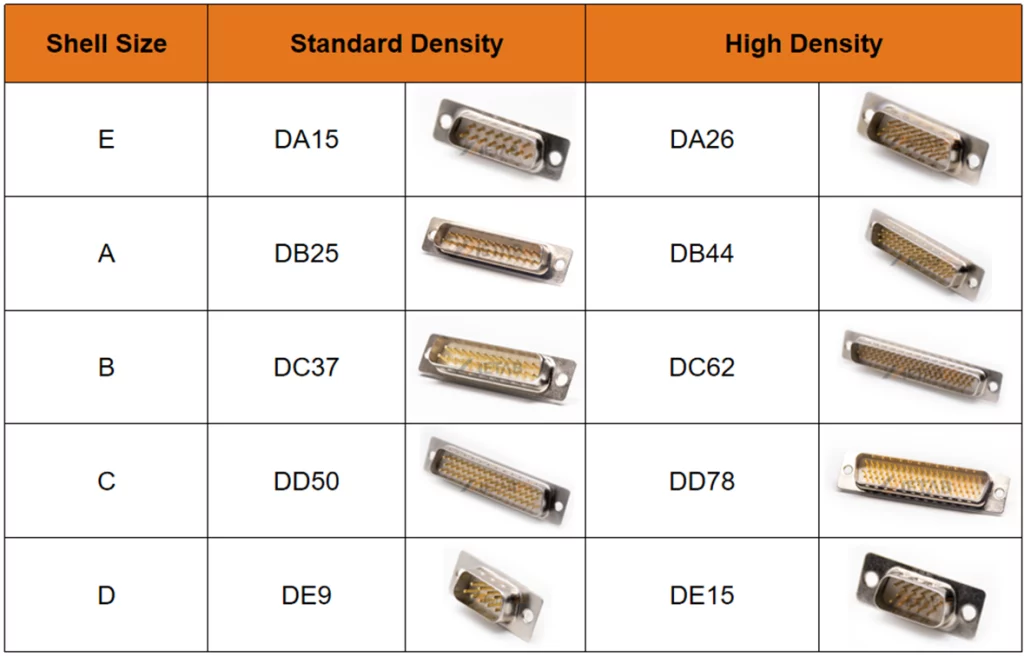
Shell Sizes
The D-Sub connector is defined by its shell sizes, which are denoted by five letters (A, B, C, D, E) corresponding to the number of pins they can hold.
- Shell Size E: The smallest shell, typically holding 9 pins (DE9) in standard density and 15 pins (DE15) in high density.
- Shell Size A: The next size up, typically holding 15 pins (DA15) in standard density and 26 pins (DA26) in high density.
- Shell Size B: A larger shell, typically holding 25 pins (DB25) in standard density and 44 pins (DB44) in high density.
- Shell Size C: Can hold up to 37 pins (DC37) in standard density and 62 pins (DC62) in high density.
- Shell Size D: The largest standard shell, holding up to 50 pins (DD50) in standard density and 78 pins (DD78) in high density.
These shell sizes and pin configurations are the foundation of the D-Sub connectors. They are allowing for a standardized approach to connecting a wide variety of devices.
The following table lists the shell sizes for various standard and high-density D-Sub connectors.
Types of D-Sub Connectors
Standard D-Sub Connectors
Standard density D-Sub connectors are the original and most traditional type. The contacts in a standard density are arranged in 2 rows. The pitch between the pins in the same row is approximately 2.77 mm (0.109 inches).
These are the five most common types:
DB9(DE9) Connector: Although people often call it DB9, this connector is technically a DE9. Because it uses an “E” size shell. It has 9 pins and was famously used for RS-232 serial communication ports on personal computers.
DB15(DA15) Connector: The DB15 connector features an “A” size shell and 15 pins. People commonly use it in various industrial and networking applications, including data acquisition systems and specialized devices.
DB25 Connector: This connector uses a “B” size shell and has 25 pins. It was the standard for parallel printer ports on early PCs and is still used in various industrial and professional audio applications.
DB37(DC37) Connector: It uses a “C” size shell with 37 pins. People commonly use it in industrial automation and telecommunications equipment, where users require a higher number of I/O lines.
DD50 Connector: The largest of the standard D-Sub connectors, using a “D” size shell with 50 pins. It is used in applications that require a high number of signal lines, such as complex data acquisition systems.

High Density D-Sub Connectors(HD)
High-density D-Sub connectors can offer a greater pin count within the same shell size because they arrange the pins in a more compact pattern. As a result, this design allows for a significant increase in data transmission lines without changing the connector’s physical footprint. Moreover, their pin pitch is 2.29mm (0.090 inches), and this width is narrower than what is used for standard density.
There are six common types of high-density D-Sub connectors:
HD15 (DE15) Connector: Uses an “E” size shell to accommodate 15 pins, arranged in 3 rows. Commonly used for VGA video connectors on computers and monitors, as well as in professional audio and video equipment.
DB26 (DA26) Connector: Uses an “A” size shell to accommodate 26 pins, arranged in 3 rows. Often found in industrial control systems and data acquisition applications.
DB44 Connector: Uses a “B” size shell to accommodate 44 pins, arranged in 3 rows. Used in various networking and telecommunication systems, where more signal lines are required in a compact space.
DB62 (DC62) Connector: Uses a “C” size shell to accommodate 62 pins, arranged in 4 rows. Ideal for high-density I/O (Input/Output) applications in complex electronic systems, such as automated test equipment.
DB78 (DD78) Connector: Uses a “D” size shell to accommodate 78 pins, arranged in 4 rows. Mainly used in specialized military and aerospace equipment, where reliability and high pin count are critical in a limited footprint.
104 Pin Connector: Uses a “6” size shell to accommodate 104 pins, arranged in 5 rows. Offering an incredibly high density for its size. This type is used in advanced data transmission and high-speed computing applications.

Combination D-Sub Connectors
Combination D-Sub connectors are a hybrid solution that integrates different types of contacts (such as signal, power, and coaxial) into a single shell. This design is highly advantageous for consolidating multiple functions into a single connection point. It significantly reduces the number of required connectors and cables. For example, people can use a Combo D-Sub connector to transmit both power and data to a device, simplifying the cabling process.
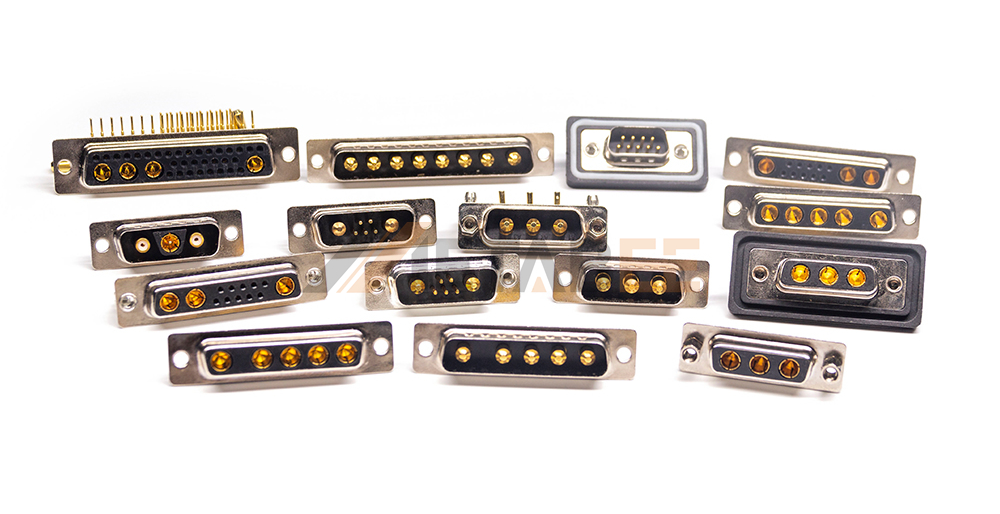

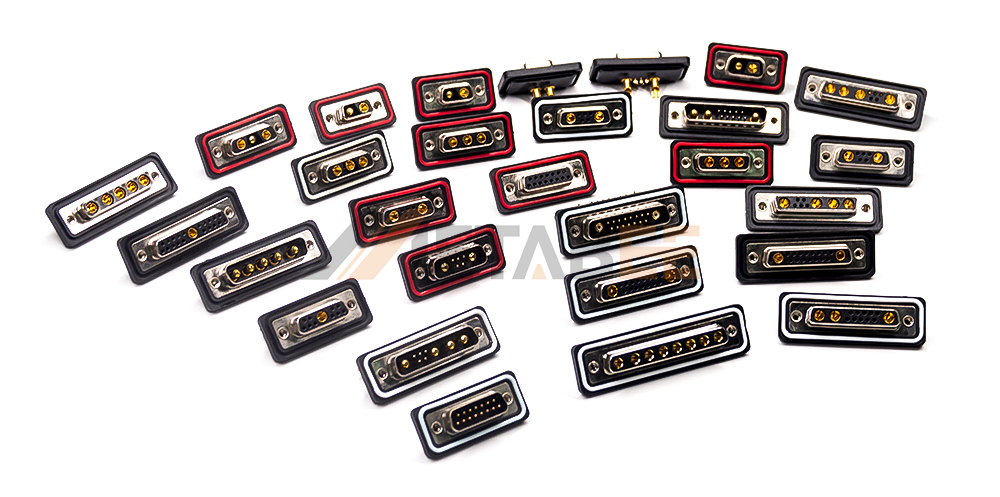
Waterproof D-Sub Connectors
Waterproof D-Sub connectors can be an ideal choice for applications in harsh or wet environments. These connectors are sealed to prevent the ingress of water and other liquids. They ensure reliable performance even when exposed to moisture.

Key Specifications
When choosing a D-Sub connector, several key specifications must be considered to ensure it meets the application’s requirements.
Gender
Like many connectors, D-Subs come in male and female versions.
- Male Connectors (Plug): These have protruding solid pins to insert into the corresponding sockets. It is typically the cable-mounted end of a connection.
- Female Connectors (Socket): These have recessed sockets that accept the male pins. It is commonly found as a PCB-mounted receptacle.
Mounting Types
How the connector integrates into your system is a key practical consideration.
- Cable Mount: The connector is terminated at the end of a cable. Termination methods include solder cups, crimping, or insulation displacement contacts (IDC).
- PCB Mount: The connector is designed to be soldered directly onto a PCB (printed circuit board).
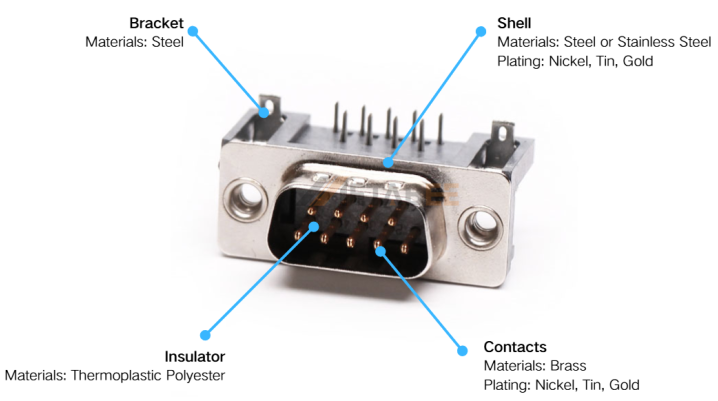
Material
The materials used are directly linked to the connector’s performance, durability, and cost.
- Shell: The outer shell is typically made from steel, which provides excellent mechanical strength. It is often plated with nickel or zinc for corrosion resistance. This plating ensures the long-term effectiveness of the electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding.
- Insulator: The internal plastic block that holds and aligns the contacts is called the insulator. It is commonly made from thermoset plastics like DAP (Diallyl Phthalate) or PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate). These materials offer high dielectric strength and thermal resistance.
- Contacts: The pins and sockets are precision-stamped and formed from copper alloys like brass or phosphor bronze for optimal spring performance and conductivity. They are commonly made of brass. These contacts are then plated with a thin layer of gold or tin over nickel. This layer is to ensure low resistance and prevent corrosion.
Electrical Specifications
- Current Rating: The maximum continuous current a single contact can carry. Standard signal pins are typically rated for 5A per pin. High-power variants or combo D-Subs can feature contacts rated for 10A, 20A, 30A, or even 40A.
- Voltage Rating: The insulator design determines a maximum voltage of 500V AC/DC between adjacent contacts. This rating provides for safe operation in most industrial and commercial environments.
- Contact Resistance: A mated contact pair should present very low electrical resistance, typically less than 20 milliohms (mΩ). Therefore, it ensures minimal signal loss and voltage drop.
- Insulation Resistance: The resistance between any contact and another contact or the shell. This is a measure of the insulator’s effectiveness. A standard value is less than 1000mΩ (at 500V DC), preventing current leakage and crosstalk.
Common Applications
Despite their age, D-Sub connectors are far from obsolete. Their robustness and reliability make them the preferred choice in many industries.
Computers and Peripherals
While modern computers have moved to USB and other interfaces, D-Sub connectors were the backbone of older systems.
- DB9: Used for RS-232 serial communication for connecting modems, mice, and other devices.
- DB25: Used for parallel ports to connect printers and other peripherals.
- HD15: Still the standard for VGA ports on monitors and projectors.
Industrial and Military Use
The rugged nature of D-Sub connectors makes them ideal for harsh environments.
- Industrial Automation: Used for connecting control systems, sensors, and robotics.
- Aerospace and Military: Their reliability under vibration and extreme temperatures is critical in avionics and military equipment.
- Test and Measurement: Used in laboratory equipment and test instruments for connecting probes and sensors.
Telecommunications and Networking
People use D-Sub connectors in a variety of telecommunications equipment for data and signal transmission.
- Network Equipment: Found on switches, routers, and other communication devices.
- Data Acquisition: Used to connect devices that collect and transmit data from various sources.
Key Manufacturers
The D-Sub connector market is served by numerous reputable manufacturers known for their quality and innovation.
TE Connectivity: TE Connectivity is a major player in the electronics industry. The company provides a comprehensive line of D-Sub connectors, which includes high-density and ruggedized versions.
Amphenol: A global leader in interconnect solutions, offering a vast portfolio of D-Sub connectors for various applications.
Norcomp: A specialized manufacturer focused on D-Sub connectors and related connectors, known for its high-quality and reliable products.
Renhotec: Renhotec is a manufacturer that provides a diverse selection of D-Sub connectors. They offer both standard and custom solutions for different electronic industries.
Metabee: Metabee is a trusted provider specializing in interconnection solutions. We offer a comprehensive range of D-Sub connectors, supplying high-quality, reliable connectors for diverse commercial and industrial needs.
How to Choose the Right D-Sub Connector
Selecting the correct D-Sub connector requires a careful evaluation of the application’s needs.
- Pin Count: First, count the number of signals or power lines you need to connect. This will help you narrow down the appropriate shell size and pin layout.
- Environment: Consider where you will use the connector. For harsh or outdoor environments, a waterproof (IP-rated) or ruggedized version is essential. For clean, indoor applications, a standard density will suffice.
- Electrical Requirements: Determine the current and voltage ratings for your application. If you need to combine different types of connections (e.g., power and signal), a Combo D-Sub connector is the best choice.
- Mounting Style: Decide whether you need a connector for a cable, or a printed circuit board.
- Shielding: For applications sensitive to EMI/RFI, ensure the connector has a robust metal shell and, if necessary, an additional shielded cable assembly.
Conclusion
The D-Sub connector was invented in the 1950s and has proven to be a durable, reliable, and versatile solution. It is still widely used in modern industrial and specialized systems today. Its distinctive design, combined with a wide range of variations, has cemented its place in electronics. These options range from standard-density to waterproof and combination types.
Although newer technologies have replaced D-Sub connectors in some consumer applications, they remain a critical component in countless mission-critical systems. This is because these applications demand paramount reliability and performance. Therefore, understanding the D-Sub connector’s history, types, and specifications is key to harnessing its full potential in your next project.
Related Products:
- D-Sub Connectors
- Standard D-Sub Connectors
- High-Density D-Sub Connectors
- Combo D-Sub Connectors
- Waterproof D-Sub Connectors

FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a DB9 and an HD15 connector?
A: Their pin count and primary functions (data vs. video) are the key differences. A DB9 connector has 9 pins and is commonly used for serial communication (like RS-232). An HD15 connector has 15 pins arranged in three rows and is the standard connector for VGA video cables.
Q: Is VGA a D-Sub connector?
A: Yes. The VGA connector is a specific type of D-Sub connectors. More precisely, the standard VGA connector is an HD15 (or DE15) connector. It has 15 pins arranged in three rows.
D-Sub connectors, which includes the DB9 (serial), DB15 (game port), and the HD15 (VGA). So, while all VGA connectors are D-Sub connectors, not all D-Sub connectors are VGA connectors.
Q: Are D-Sub connectors still used today?
A: Yes. D-Sub connectors are still used today, but their prevalence has declined in consumer applications. They remain common in specific industrial, manufacturing, and commercial sectors due to their durability, reliability, and screw-locking mechanism.
Q: Can I plug a Standard Density cable into a High-Density port?
A: No. They are not compatible. A Standard Density (e.g., DB9) connector has fewer pins and rows than a High-Density (e.g., HD15) port. Attempting to plug them together will likely bend or break the pins, causing damage.
Q: What are the screws on the side for?
A: The screws attach to threaded inserts on the mating connector. This creates a secure and locked connection. It prevents the cable from accidentally coming loose from vibration or pulling.
Q: What does “current rating” mean for a D-Sub connector?
A: The current rating is the maximum electrical current each pin can safely carry. Exceeding this rating can cause overheating and damage. For most standard signal pins in a D-Sub connector, this rating is typically quite low (around 3 A to 5 A).
Q: Why would I choose a D-Sub connector instead of a USB or DBMI connector?
A: D-Sub connectors offer superior mechanical robustness, better EMI shielding with metal shells, and the ability to be secured with screws. This makes them ideal for permanent installations and harsh industrial environments where a secure connection is critical.
Q: Can I use a male and a female connector from different manufacturers?
A: Yes, as long as the pin counts match. While standardized pin layouts ensure basic function, the quality and plating of the pins (like gold vs. tin) can vary between manufacturers. This can affect the connector’s durability, corrosion resistance, and long-term electrical performance.
Pingback: What is a DB25 Connector? A Deep Dive into this D-Sub Connector - MetabeeAI
Pingback: DB15 vs VGA: The Surprising Differences Between DB15 and VGA - MetabeeAI
Pingback: The Complete Guide to the Standard DB50 Connector MetabeeAI