As electric vehicles (EVs) gain global adoption, EV charging infrastructure has become a critical component of the transportation ecosystem. At the core of this infrastructure are EV charging connector types, which determine charging compatibility, speed, safety, and regional usability. We will provide a comprehensive explanation of the five most common EV charging connector types—GB/T, IEC, SAE, CCS, and CHAdeMO—covering their standards, designs, technical specifications, and future development.
- Basics of the EV Charging Connector
- Types of EV Charging Connectors
- GB/T EV Charging Connectors (China Standard)
- IEC Type 2 EV Charging Connectors (Europe Standard)
- SAE J1772 Type 1 EV Charging Connectors (North American AC Standard)
- CCS EV Charging Connectors
- CHAdeMO EV Charging Connectors (Japan Standard)
- How to Choose the Right EV Charging Connector Types?
- The Leading EV Charging Connector Factories and Manufacturers
- Conclusion
- Related Products
Basics of the EV Charging Connector
Before diving into specific charging standards, it is vital to understand the fundamental knowledge related to EV charging.
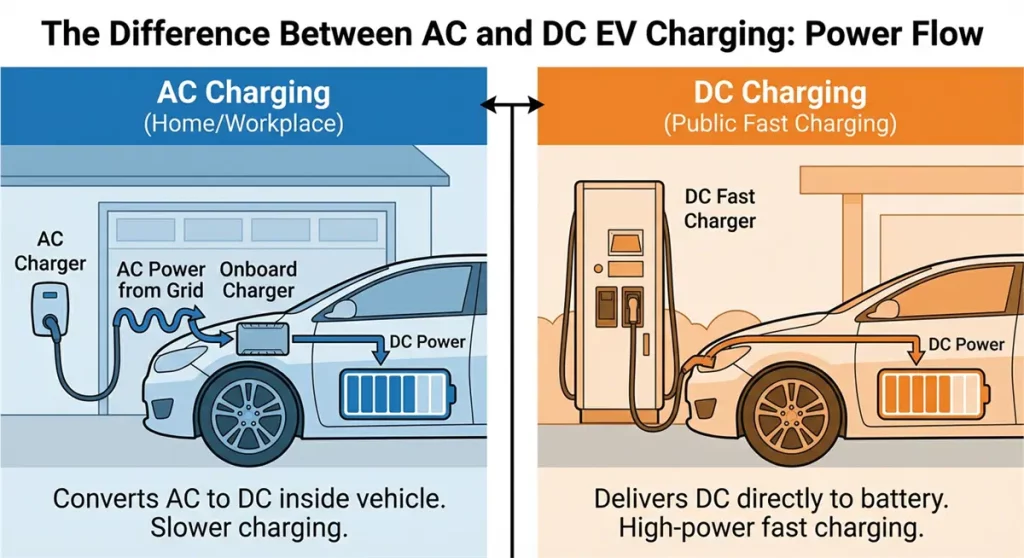
AC vs DC charging
EV charging is broadly divided into AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) charging:
- AC Charging (Alternating Current): This charging converts AC power from the grid into DC power inside the vehicle using the onboard charger. This method is common for home and workplace charging.
- DC Charging (Direct Current): This charging delivers DC power directly to the vehicle battery, bypassing the onboard charger. This enables high-power fast charging, typically used at public charging stations.
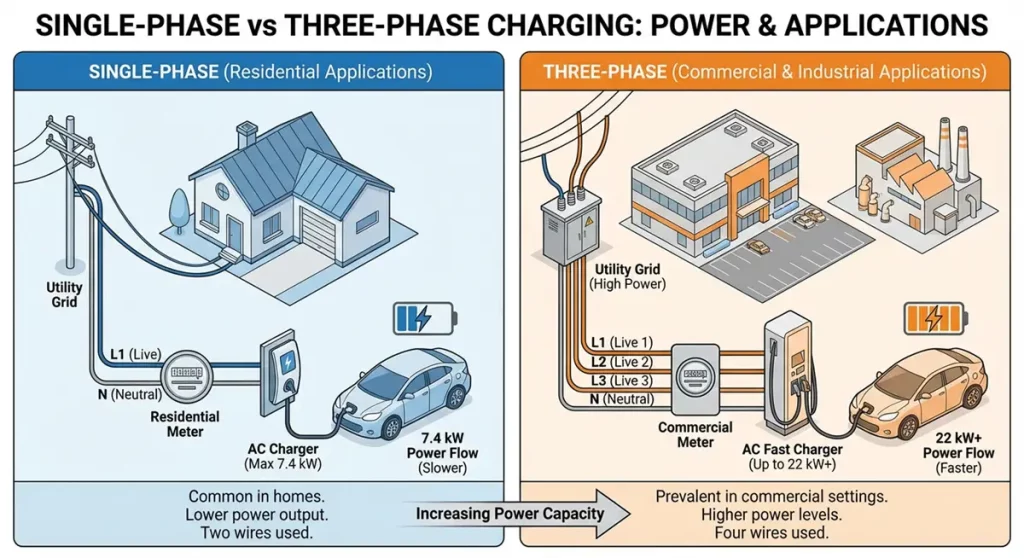
Single-phase vs Three-phase charging explained
- Single-phase: Uses two wires (L1 and Neutral). Common in residential applications, offering lower power output (typically up to 7.4 kW).
- Three-phase: Uses four wires (L1, L2, L3, and Neutral). Prevalent in commercial settings and industrial environments, supporting higher power levels (up to 22kW or more for AC charging).
Why EV Charging Connector Types Matter?
Incompatibility is a major barrier to EV adoption. While the connector type determines where and how quickly an EV can charge. So choosing the correct EV charging connector type is essential for ensuring safety, efficiency, and long-term compatibility.
Different EV charging connector types determine:
- Charging speed and power capacity
- Regional and vehicle compatibility
- Infrastructure investment decisions
- Future scalability of charging systems
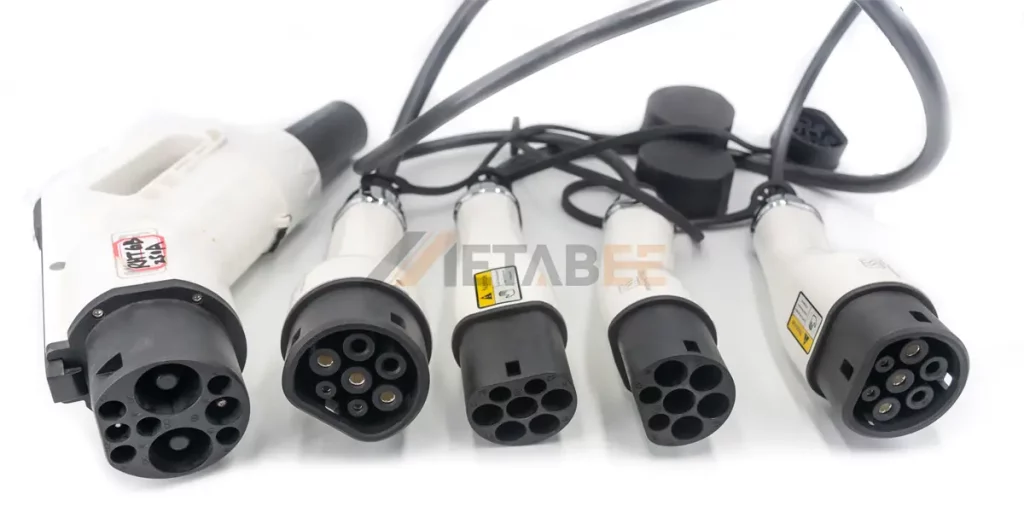
Types of EV Charging Connectors
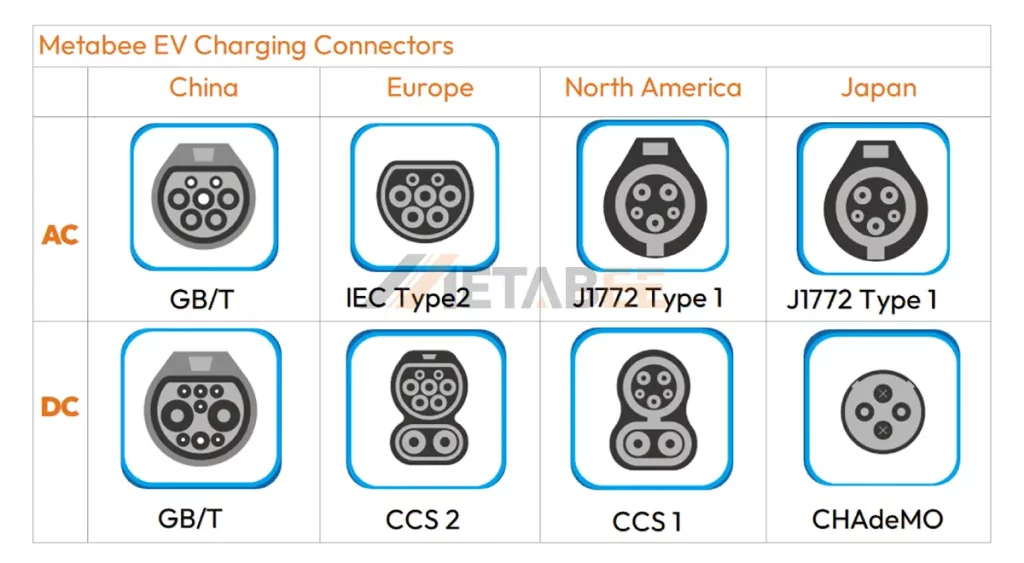
Globally, EV charging connectors are standardized by different organizations and regions. Below are the 5 common EV charging connectors types.
Quick Reference Comparison Table
GB/T EV Charging Connectors (China Standard)

GB/T EV Charging Connectors
Definition
The GB/T (Guobiao) standard is the national mandatory standard in China. Unlike other systems, GB/T uses separate connectors for AC and DC charging. Given China’s status as the world’s largest EV market, the GB/T connector is the most widely produced plug globally.
Dual-Port Design
GB/T vehicles typically feature two separate inlets: one for AC (slow) and one for DC (fast).
This dual-port design allows optimized performance for each charging mode.
- GB/T AC Connectors: A unique, rounded rectangular connector with 7 pins. They are similar in appearance to the IEC Type 2 but with reversed male/female pin assignments. In the GB/T system, the charging cable has a male plug, and the vehicle has a female inlet.
- GB/T DC Connectors: A larger, circular connector with 9 pins and prominent cooling vents. They are for high-current throughput and digital communication via CAN bus.
Plug and Socket of GB/T AC Charging Connnectors

Plug and Socket of GB/T DC Charging Connnectors

Technical Specifications
| Specification | GB/T AC | GB/T DC |
|---|---|---|
| Output Current Type | AC (Alternate Current) | DC Direct Current) |
| Voltage | 250V / 440V | 750V |
| Current | 10A / 16A / 32A | Up to 250A |
| Max Power | Up to 22 kW | Up to 250 kW+ |
| EV Charging Level | Level 2 | Level 3 (DC fast charging) |
| Main Countries | China | China |
Compatibility and the Future
GB/T connectors dominate the Chinese EV market. With the development of the ChaoJi ultra-high-power charging standard, GB/T is evolving to support next-generation EV platforms.
IEC Type 2 EV Charging Connectors (Europe Standard)
Definition
IEC Type 2 connectors, often referred to as the “Mennekes” plug, are standardized under IEC 62196-2. In 2014, the European Commission mandated the Type 2 connector as the standard for all public AC charging stations. They have been adopted by many other countries, including Australia and parts of South America. They support Mode 2 and Mode 3 charging and leverage Europe’s widespread three-phase electrical grid, making it significantly more powerful and efficient for commercial and industrial applications.
Design & Pins
The IEC Type 2 connector features a circular design with a flat top and a 7-pin design. It is uniquely versatile because it can handle both single-phase and three-phase power.
IEC Standard AC Charging Type
Technical Specifications
| Specification | IEC Type 2 |
|---|---|
| Output Current Type | Single and Three-phase AC |
| Voltage | Up to 480V |
| Current | 16A / 32A / 63A |
| Max Power | Single-phase: up to 7.4 kW Three-phase: up to 22 kW |
| EV Charging Level | Level 2 |
| Main Countries | Europe, United Kingdom, Middle East, Africa, Australia |
SAE J1772 Type 1 EV Charging Connectors (North American AC Standard)
What is J1772 Charging?
The SAE J1772 standard, or “Type 1 or J-plug,” is the universal AC charging connector for North America and Japan. It is the primary connector for Level 1 (120V) and Level 2 (240V) charging.
J1772 is designed specifically for single-phase AC electrical systems, making it perfectly suited for residential and light commercial grids in its target markets.
Design & Pins
The SAE J1772 connector features a circular 5-pin layout with a physical latch that the user must press to engage or disengage the plug.
SAE J1772 Standard:
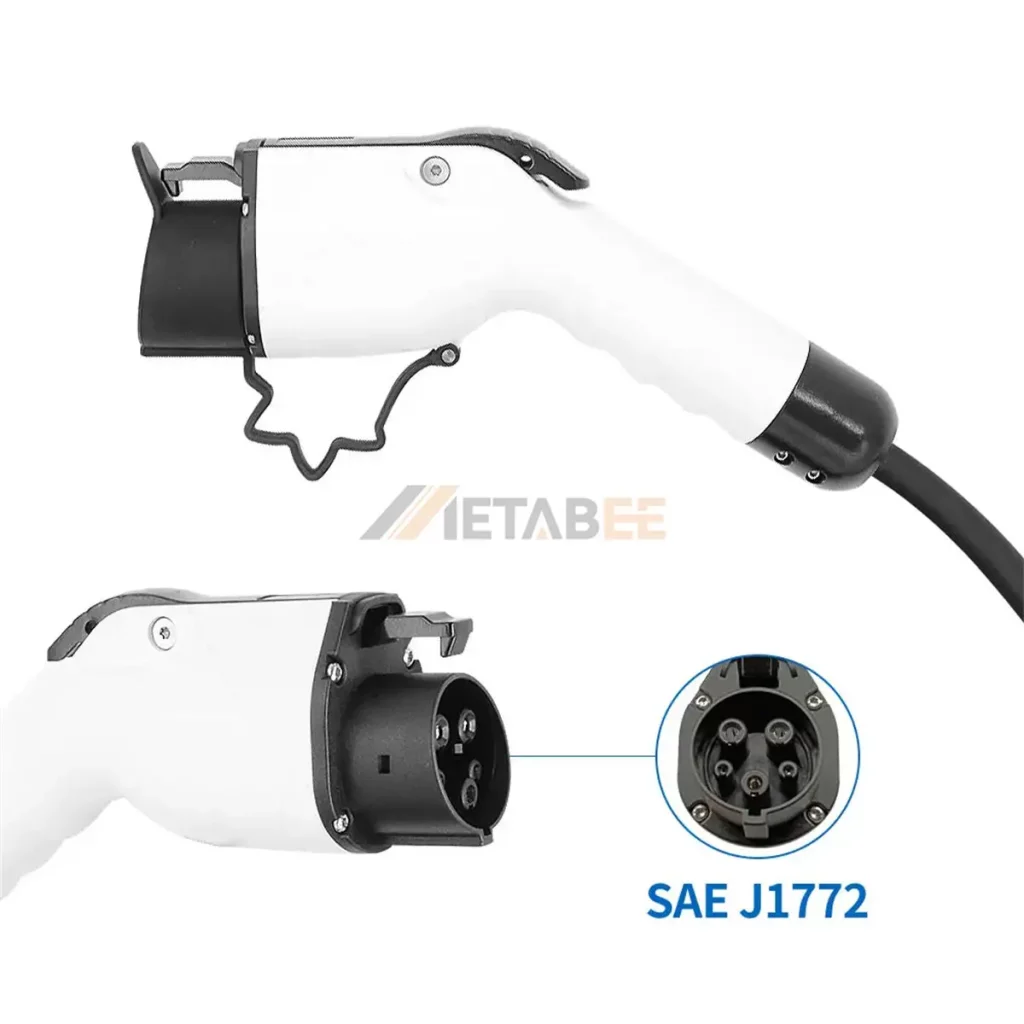

Plug and Socket of SAE J772 Charging Connectors:
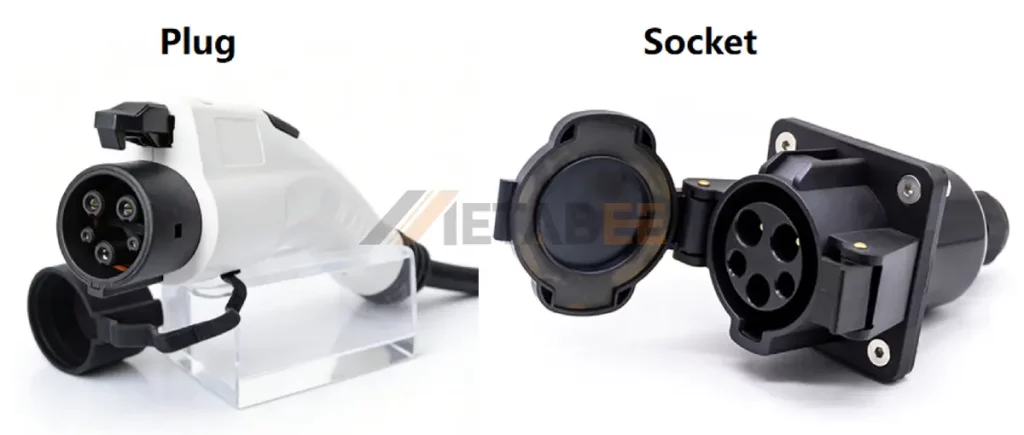

Technical Specifications
| Specification | SAE j1772 (Type 1) |
|---|---|
| Output Current Type | Single-phase AC |
| Voltage | 240V |
| Current | Up to 80A |
| Max Power | Up to 19.2 kW. |
| EV Charging Level | Level 1, Level 2 |
| Main Countries | USA, Canada, Japan |
Limitations
The primary limitation of Type 1 is its lack of support for three-phase power, which makes it less efficient for high-capacity industrial applications compared to the European Type 2.
CCS EV Charging Connectors
What is CCS Charging?
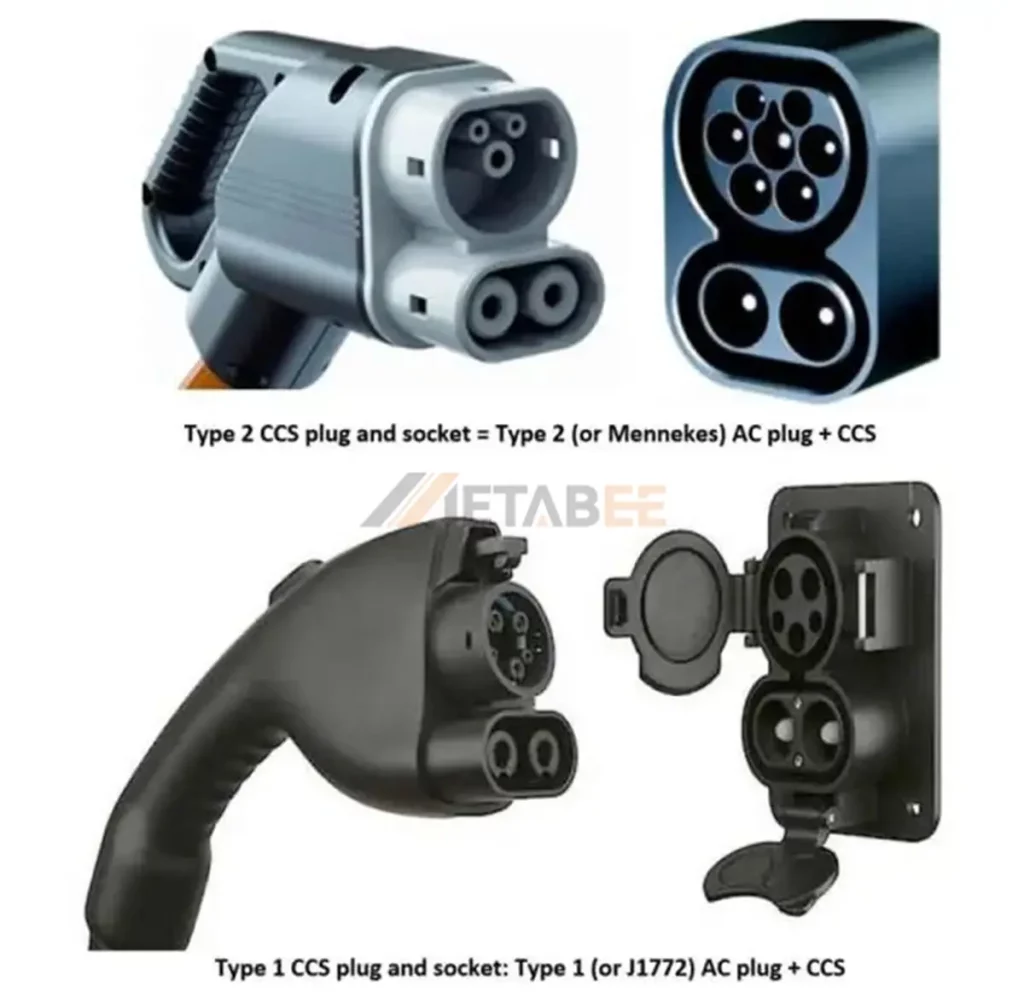
The CCS (Combined Charging System) is one of the most widely adopted EV fast-charging standards globally. The “Combined” in CCS refers to its ability to integrate the existing AC charging standards (Type 1 and Type 2) with two additional high-voltage DC power pins. CCS is an “enhanced” version of the Type 1 and Type 2 connectors. It adds two large DC pins at the bottom, allowing the same port to be used for both AC and DC charging. This design reduces the footprint of the charging inlet on the vehicle and simplifies the user experience.
CCS1 vs CCS2
While the “Combined” concept is the same globally, the physical implementation differs based on the regional AC standards. The CCS standard is divided into two primary versions:
CCS1
The Combined Charging System Type 1 (CCS1) connector, also known as Combo 1 or the SAE J1772 Combo, provides a single, integrated solution for both AC and DC charging. Its design combines the standard SAE J1772 (Type 1) AC connector with two additional DC pins. While this standard is predominant in North America, Canada and South Korea, its reliance on the Type 1 connector introduces a key limitation: CCS1 does not support three-phase AC charging.
CCS2
The Combined Charging System Type 2 (CCS2), or Combo 2, integrates the IEC 62196 Type 2 connector with two additional DC pins to support both AC and DC charging from a single port. CCS2 supports three-phase AC charging. This allows for higher power AC charging, making it a more efficient solution for commercial and public charging stations.
CCS1 andc CCS2 Charging Type

Quick Comparison Table
| Feature | CCS1 (Combo 1) | CCS2 (Combo 2) |
|---|---|---|
| Base AC Connector | SAE J1772 (Type 1) | IEC 62196-2 (Type 2) |
| Phases | Single-phase AC only | Single-phase & Three-phase AC |
| Physical Design | Features a latching mechanism on the plug | Features a locking mechanism within the vehicle inlet |
| EV Charging Level | Level 3 (DC fast charging) | Level 3 (DC fast charging) |
| Primary Region | North America, Canada and South Korea | Europe, Oceania, and much of Asia |
| Market Trend | Transitioning toward NACS in North America | The dominant global standard for high-power charging |
Technical Specifications
The CCS standard is engineered for high performance and scalability, making it the preferred choice for the latest “Ultra-Fast” charging networks.
| Specification | CCS1 | CCS2 |
|---|---|---|
| Output Current Type | DC (Direct Current) | DC (Direct Current) |
| Voltage | 1000 Volts DC | 1000 Volts DC |
| Current | 125A, 150A | 150A |
| Max Power | 350 kW | 350 kW |
| EV Charging Level | Level 3 (DC fast charging) | Level 3 (DC fast charging) |
| Main Countries | North America, Canada and South Korea | Europe, Oceania, and much of Asia |
CHAdeMO EV Charging Connectors (Japan Standard)
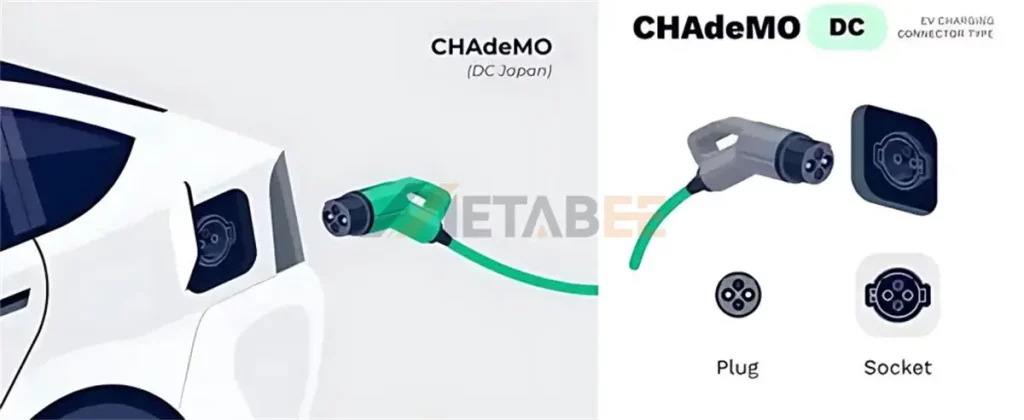
CHAdeMO is a well-established DC fast charging standard developed in Japan and widely recognized as one of the earliest solutions for high-power electric vehicle charging.
Definition
The name CHAdeMO is an abbreviation of “CHArge de MOve” (moving by charge). Established in 2010 by the CHAdeMO Association (formed by the Tokyo Electric Power Company, Nissan, Mitsubishi, and Toyota), this standard was designed to solve the “range anxiety” of early EV adopters. While newer standards like CCS have gained dominance in Europe and North America, CHAdeMO remains the primary standard in Japan and continues to be valued worldwide for its unique bidirectional charging capabilities.
Design & Pins
CHAdeMO is a dedicated DC-only connector. It features two separate ports: a CHAdeMO port for fast charging and a Type 1 or Type 2 port for home AC charging. And it is known for its robust, round shape and a complex 10-pin configuration.
DC Charging CHAdeMO Standard
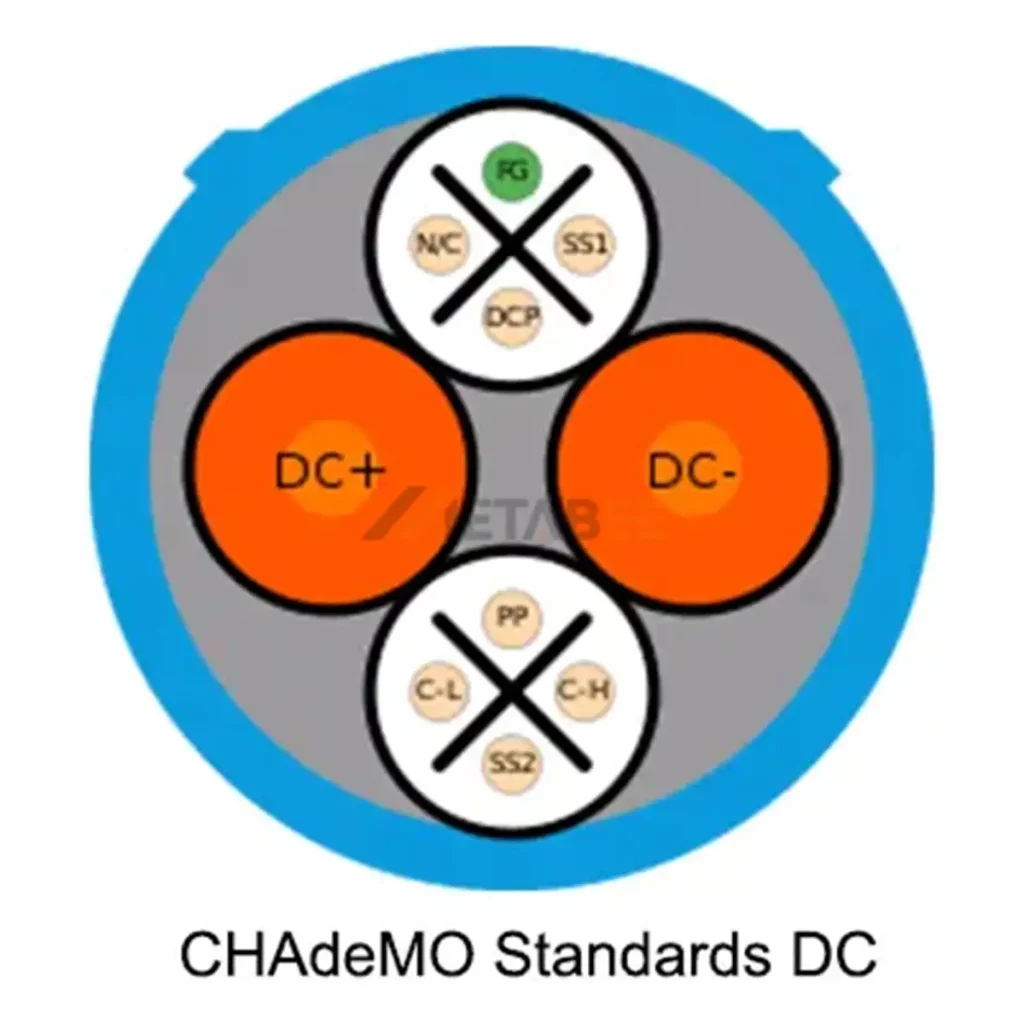
CHAdeMO Charging Connectors

Technical Specifications
CHAdeMO has evolved through several iterations to keep pace with increasing battery capacities. Below are the technical specifications for the most common versions:
| Specification | CHAdeMO |
|---|---|
| Output Current Type | DC (Direct Current) |
| Voltage | 1000 V |
| Current | 125A |
| Max Power | 65 kW |
| EV Charging Level | Level 3 (DC fast charging) |
| Main Countries | Japan |
How to Choose the Right EV Charging Connector Types?
Selecting the correct EV charging connector is not just a matter of “plug and play.” It requires a strategic understanding of regional electrical standards, vehicle specifications, and the intended use case. It will directly affect charging compatibility, efficiency, and long-term usability. For EV owners, fleet operators, and charging infrastructure planners, the choice should be based on several key technical and practical factors.
Region
Geography is the primary factor in determining connector compatibility. The global EV market is fragmented into several major standards based on the local power grid and regulatory frameworks:
- North America: Historically dominated by the SAE J1772 (Type 1) for AC and CCS1 for DC. However, the NACS (Tesla) standard is rapidly becoming the new benchmark.
- Europe: The IEC 62196 Type 2 (Mennekes) is the mandatory standard for AC charging, while CCS2 is the standard for DC fast charging.
- China: All vehicles and chargers must adhere to the GB/T national standard (separate ports for AC and DC).
- Japan: Uses Type 1 for AC and CHAdeMO for DC.
Vehicle Type
The type of electric vehicle dictates the power requirement:
- Plug-in Hybrids (PHEVs): These typically have smaller batteries and limited onboard chargers. Most PHEVs only require AC connectors (Type 1 or Type 2) and rarely support DC fast charging.
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): Since BEVs rely solely on electricity, they require both AC for overnight charging and DC connectors (CCS, CHAdeMO, or GB/T) for rapid “en-route” charging during long trips.
Charging Speed
The connector must be able to handle the amperage and voltage required for your desired charging speed:
- Level 1 & 2 (AC Charging): Best for residential and workplace settings. Choose a Type 1 or Type 2 connector. Type 2 is particularly versatile, as it supports three-phase charging, allowing for speeds up to 22kW.
- Level 3 (DC Fast Charging): Essential for commercial hubs and highway stations. CCS and GB/T DC connectors are designed for high-voltage throughput, often reaching 150kW to 350kW or more.
Interface Compatibility
The simple rule of compatibility is that the plug from the charging station must fit the inlet on your vehicle. Key aspects to consider include:
- Pin configuration and locking mechanisms
- Communication protocols (PLC, CAN, ISO 15118 support)
- Thermal management and current limits
- Backward compatibility and adapter availability
Infrastructure
Before selecting a connector type for installation, evaluate your local electrical infrastructure:
- Domestic vs. Commercial: For residential use, simple AC connectors (Type 1 or Type 2) are standard.
- Public Charging Networks: For Public infrastructure, a multi-standard approach (e.g., a charger equipped with both CCS2 and CHAdeMO cables) is often the best strategy to maximize user reach and ROI.
The Leading EV Charging Connector Factories and Manufacturers
For B2B buyers, sourcing from reputable manufacturers ensures compliance with UL, CE, and TUV certifications. Here are some of the famous EV charging connector manufacturers:
- TE Connectivity: It is a leading industrial technology company offering comprehensive EV charging connectors and inlets. Their AMPHENOL and specialized EV series are renowned for high-voltage ruggedness.
- Leviton: Leviton is a well-established North American manufacturer specializing in electrical wiring devices and EV charging solutions. It focus on residential, commercial, and fleet applications.
- ChargePoint: As a leading networked EV charging solution provider, ChargePoint offers software, hardware, and services. Their products includes CCS1, CHAdeMO, J1772, and Type 2, along with CCS2.
- Metabee: Metabee is an emerging EV charging connector manufacturer with a strong focus on cost-effective production and international standard compliance.
- Renhotec: Renhotec is a specialized connector manufacturer with extensive experience in EV charging connectors, power connectors, and industrial interconnect solutions.
Future Trends in EV Charging Connectors
The Rise of NACS
The North American Charging Standard (NACS), formerly Tesla’s proprietary plug, has seen massive adoption by Ford, GM, and Rivian. It is set to become the dominant DC standard in North America.
ChaoJi Standard Charging
The collaboration between China and Japan aims to harmonize GB/T and CHAdeMO, creating a safe, ultra-high-power connector for heavy-duty vehicles.
Wireless EV Charging
Inductive charging pads are moving from pilot programs to reality, potentially eliminating the need for physical connectors in premium and autonomous vehicle segments.
Conclusion
The EV charging landscape is moving toward consolidation, yet regional differences remain a vital consideration for international trade. This blog elucidated the five most prevalent connector types, highlighting their design, specifications, and regional dominance. By understanding these standards, B2B customers can better navigate the transition to green energy and make informed decisions. Choosing a reliable EV charging connector manufacturing partner ensures that your charging solutions meet the rigorous demands of tomorrow’s electric vehicle ecosystem.
Related Products
- GB/T AC Connectors
- GB/T DC Connectors
- IEC 62196-2 Type 2 Connectors
- SAE J1772 Connectors
- CCS Combined Charging System Connectors
- Chademo Charging Connectors
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1:What are the main types of EV charging connectors globally?
A: The five most common EV charging connector types are GB/T (China), IEC Type 2 (Europe), SAE J1772 (North American AC standard), CCS (Combined Charging System, including CCS1 and CCS2), and CHAdeMO (Japan). Each standard caters to specific regional requirements and vehicle types.
Q2: What is the main difference between CCS1 and CCS2?
A: It is regional: CCS1 is based on the Type 1 AC standard and is used in North America. CCS2 is based on the Type 2 AC standard and is the requirement in Europe and most other regions.
Q3: Can I use a Type 2 cable on a Type 1 car?
A: Not directly. However, you can use a Type 2 to Type 1 adapter to bridge the connection safely.
Q4: Is Tesla’s plug compatible with these?
A: In Europe, Tesla uses standard Type 2/CCS2. In North America, they use NACS, but provide adapters for J1772 and CCS1.
Q5: Is CCS better than CHAdeMO?
A: CCS is currently more widely adopted by European and American manufacturers, but CHAdeMO is superior for bi-directional charging (V2G).
Q6: What is the difference between IEC Type 2 and SAE J1772?
A: The primary difference lies in regional adoption and electrical capability.
- IEC Type 2 supports both single-phase and three-phase AC charging, enabling higher power levels and making it the dominant AC connector in Europe.
- SAE J1772 Type 1 supports single-phase AC charging only and is commonly used in North America and Japan.
Q7: What is the fastest EV charging connector?
A: Currently, CCS2 standards offer the highest power delivery, often exceeding 350kW.