In today’s rapidly evolving landscape of industrial automation, the demand for efficient, reliable, and robust connectivity solutions has never been greater. M8 and M12 circular connectors have become ubiquitous in connecting sensors, actuators, switches, and various other devices within automated systems. Their widespread adoption stems from their ability to withstand harsh conditions, including exposure to dust, moisture, vibration, and extreme temperatures. M8 vs M12: despite their shared purpose and similar design principles, M8 and M12 connectors possess distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed comparison of M8 and M12 connectors, exploring their key differences, highlighting their shared attributes, and offering practical guidance on selecting the appropriate connector for specific needs. This article will equip you with the information necessary to make informed decisions and ensure reliable connections in your industrial applications.
By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of M8 and M12 connectors, empowering you to select the optimal connectivity solution for your industrial automation needs.
Introduction of M12 and M8 Connectors
M8 and M12 connectors are circular connectors with screw-locking mechanisms commonly used in industrial automation and control systems. They provide robust and reliable connections for sensors, actuators, switches, and other devices in harsh industrial environments. The “M” designation refers to the metric thread size of the coupling nut, with “8” indicating an 8mm thread diameter and “12” indicating a 12mm thread diameter.
What is an M8 Connector?
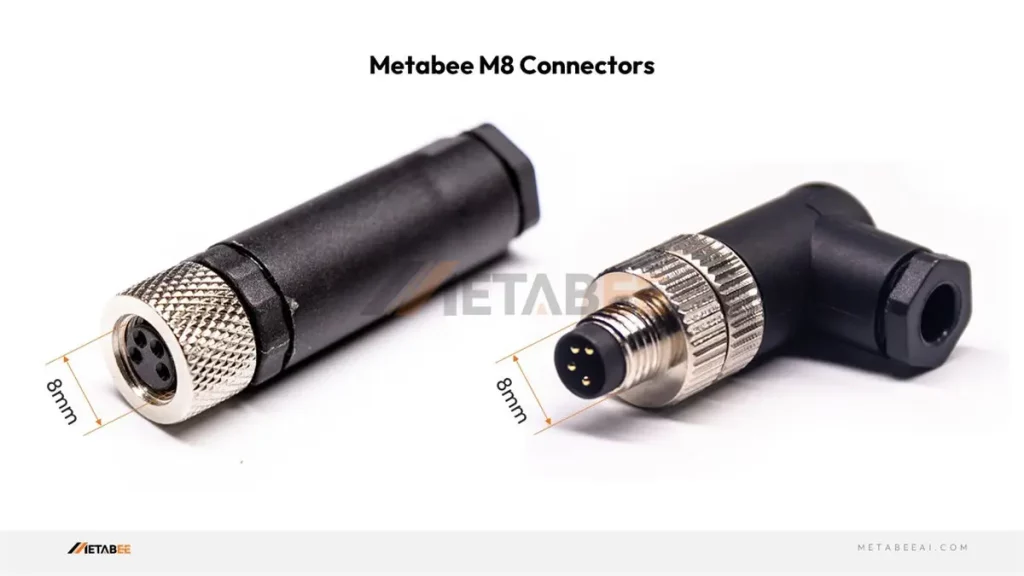
An M8 connector is a metric screw-sized circular connector with an 8mm diameter threaded coupling. It’s designed for applications where space is limited and a compact connection solution is required.

Related Post:
What is an M8 Connector? A Comprehensive Guide
Key Characteristics
- Compact Size: The small size makes it ideal for use in confined spaces.
- Screw-Locking Mechanism: Provides a secure and reliable connection resistant to vibration and accidental disconnection.
- Robust Design: Typically constructed from durable materials to withstand harsh industrial environments.
- Various Pin Counts: Available with different numbers of pins (typically 3, 4, 5, 6, and sometimes 8) to accommodate various signal and power requirements.
- IP Protection: Offers protection against dust and water ingress, typically with IP67 or IP68 ratings.
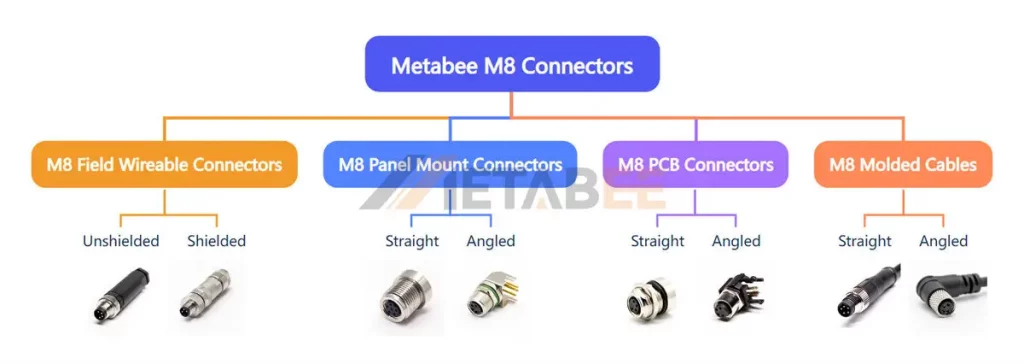
Main Types of M8 Connectors
- M8 Filed Wireable Connectors: These connectors allow for on-site assembly and customization of cable lengths and connections, providing flexibility in industrial applications.
- Panel Mount M8 Connectors: These connectors are designed for mounting on panels or enclosures to create a fixed connection point.
- M8 PCB Connectors: These connectors are designed for direct mounting onto printed circuit boards.
- M8 Overmolded Cables: They are pre-assembled connectors with attached cables, providing a ready-to-use solution.
What is an M12 Connector?
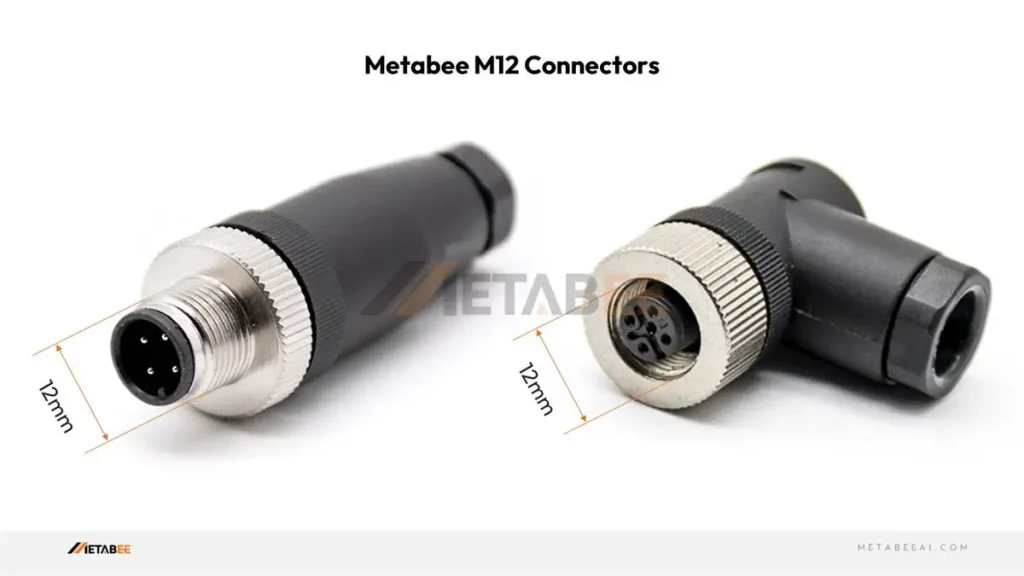
An M12 connector is a metric screw-sized circular connector with a 12mm diameter threaded coupling. Its larger size allows for higher pin counts, greater current carrying capacity, and increased robustness compared to M8 connectors.

Related Post:
What is an M12 Connector? A Complete Overview
Key Characteristics
- Increased Robustness: The larger size provides greater resistance to mechanical stress and harsh environments.
- Higher Pin Counts: Available with a wider range of pin counts (typically 3, 4, 5, 8, 12, and up to 17) to accommodate more complex signal and power requirements.
- Higher Current and Voltage Ratings: Can handle higher currents and voltages compared to M8 connectors.
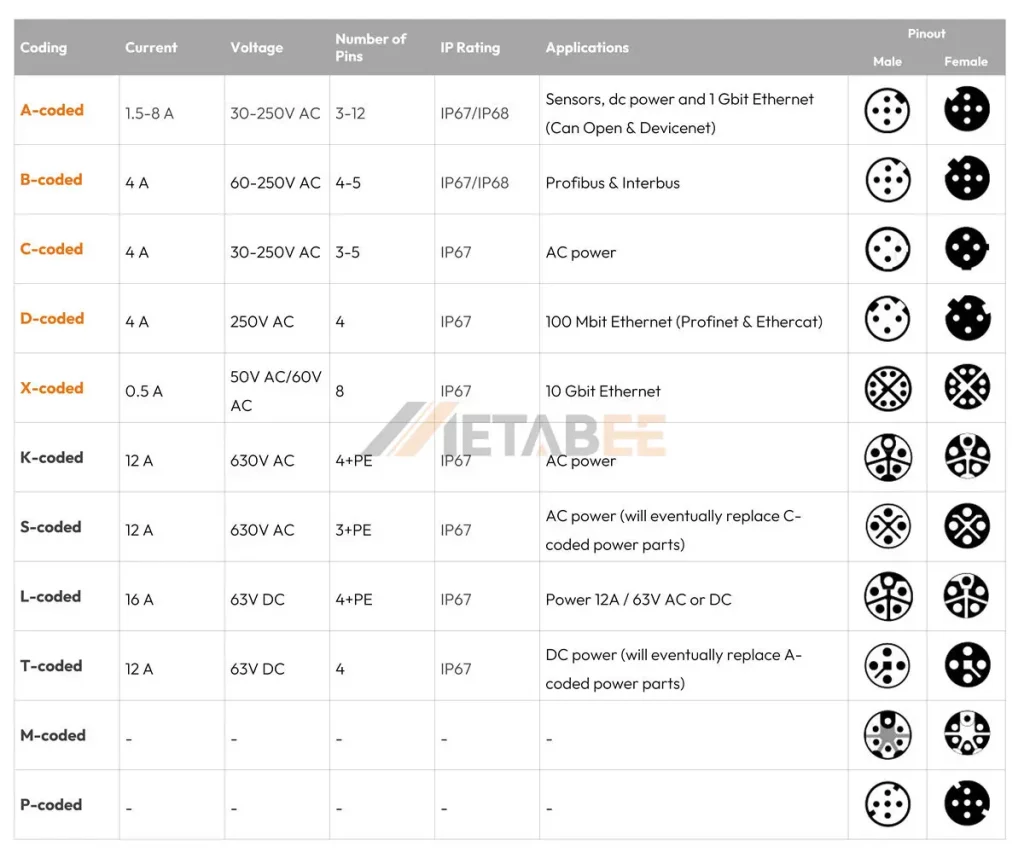
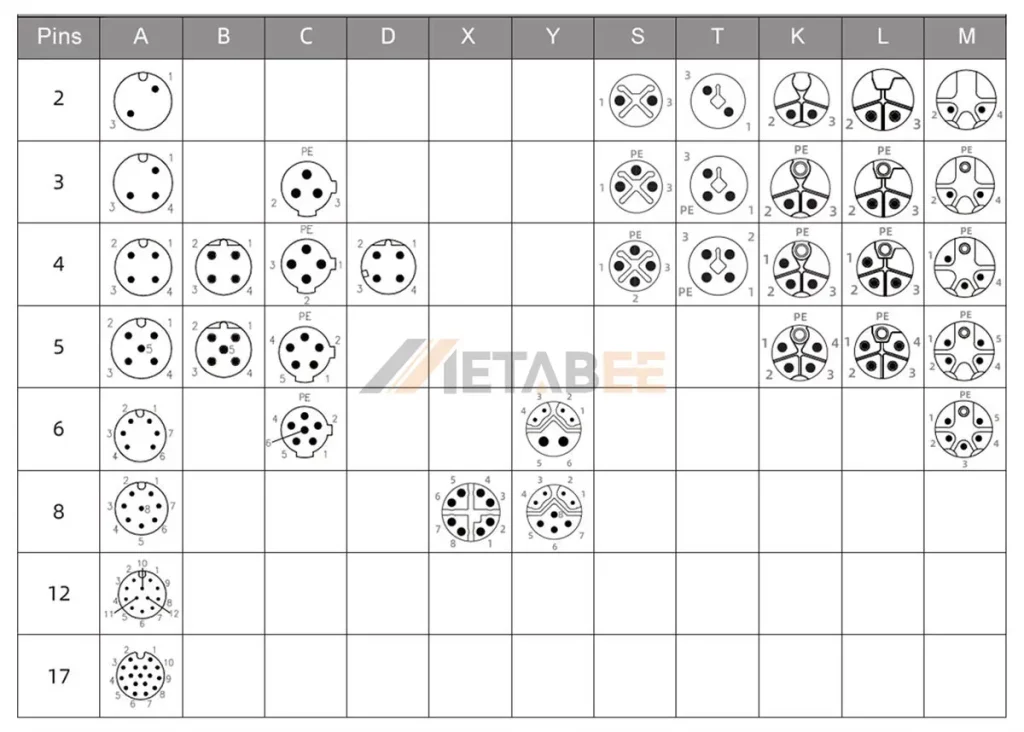
- Various Codings: Offers a wider range of codings (A, B, C, D, X, S, T, K, L, M) to prevent mismating and support various communication protocols.
- IP Protection: Offers protection against dust and water ingress, typically with IP67 or IP68 ratings.
Main Types of M12 Connectors
- M12 Field-Wireable Connectors: Allow users to attach cables in the field, providing flexibility for custom cable lengths.
- Panel Mount M12 Connectors: Designed for mounting on panels or enclosures.
- M12 PCB connectors: designed for direct mounting onto printed circuit boards.
- M12 Overmolded Cables: Pre-assembled connectors with attached cables.

Related Post:
M12 Connector Types: A Visual Guide for Identifying and Selecting the Right Connector
Key Differences Between M8 and M12 Connectors
While both M8 and M12 connectors are widely used in industrial automation, several key distinctions make them suitable for different applications. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their key differences:
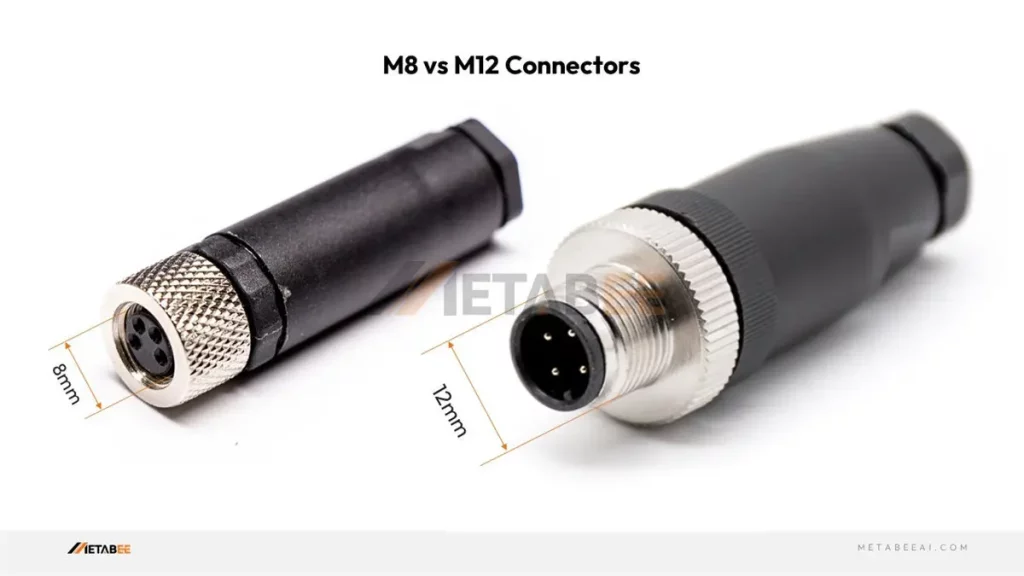
Size and Appearance
The most apparent difference is the size of the threaded coupling. M8 connectors have an 8mm diameter, while M12 connectors have a 12mm diameter. Besides, the overall length and body size of M12 connectors are also larger than M8 connectors. This allows for more robust construction and the accommodation of more pins.

Thread Specifications
The coupling interface for both M8 and M12 connectors is a metric thread. Specifically, the M8 connector utilizes an M8x1 thread, and the M12 connector utilizes an M12x1 thread.
Coding
M8 and M12 connectors utilize coding to prevent accidental cross-mating. This is particularly important in systems with multiple connectors of the same form factor, as it ensures only connectors with matching codings can be mated.
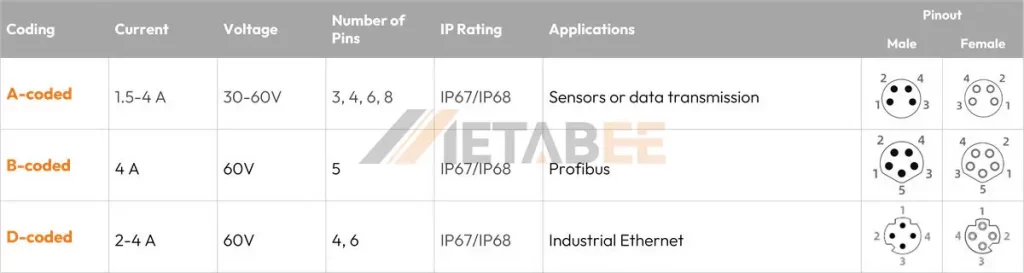
The coding schemes for M8 and M12 connectors differ significantly. M8 connectors are commonly available with A, B and D codings only, while M12 connectors offer a wider selection, encompassing A, B, C, D, X, S, T, K, L, and M codings, each designed for distinct applications.
Common Codings:
- A-coding: Primarily used for sensors, actuators, and power applications. This is the most common coding for both M8 and M12.
- B-coding: Used for PROFIBUS networks.
- C-coding: Used for Ethernet communication (typically 100 Mbit/s).
- X-coding: Used for high-speed Ethernet communication (up to 10 Gbit/s). This is more common in M12 due to its higher bandwidth capabilities.
- S-coding: Used for AC power applications.
- T-coding: Used for DC power applications.
While A-coding and B-coding are available for both M8 and M12, other codings are more prevalent in M12 due to its greater versatility.
Coding System of M8 Connectors
Coding System of M12 Connectors
Number of Pins
M8: Typically available with 3, 4, 5, 6, and sometimes 8 pins.
The M8 connector pinout is shown in the figure below:
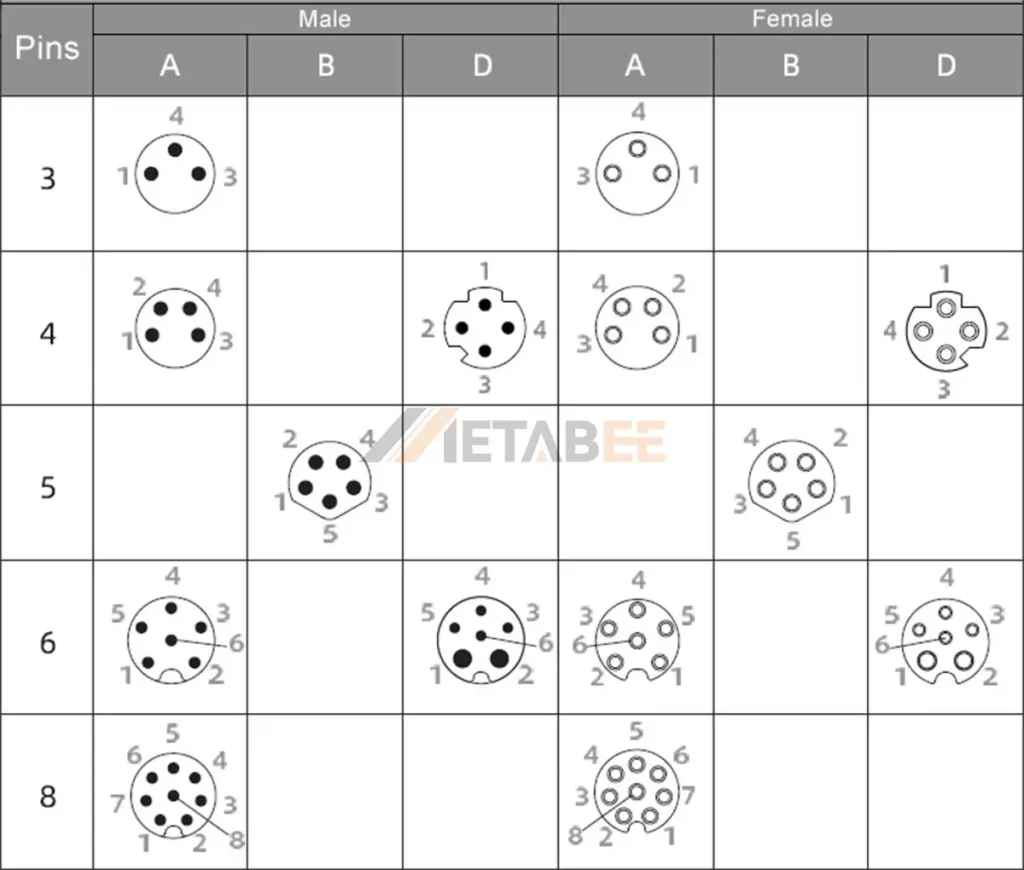
M12: Available with a wider range of pin counts, including 3, 4, 5, 8, 12, and even 17 pins.
The M12 connector pinout is shown in the figure below:
Related Post:
The Ultimate Guide to M12 Connector Pinout, Color Code, and Wiring Diagram
The number of pins directly relates to the number of signals or power connections that can be transmitted. Higher pin counts allow for more complex functionalities and data transmission.
Standards
The primary standard governing M8 and M12 connectors is the IEC 61076-2 series. The IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) is a global standards organization that publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic, and related technologies. It plays a crucial role in ensuring interoperability, safety, and quality in electrical and electronic devices and systems worldwide.
This series of standards specifically addresses connectors used in various electrical and electronic applications. Within this series, different parts focus on specific connector types and their requirements.
Standard List for IEC M8 and M12 metric screw sized connectors:
M8 Connector Standards:
- IEC 61076-2-104 M8 connectors with screw-locking or snap-locking: M8 A and B-coding
- IEC 61076-2-114 M8 connectors with screw-locking, power and signal contacts for data transmission frequencies up to 100 MHz: M8 D and P-coding
M12 Connector Standards:
- IEC 61076-2-101 M12 connectors with screw-locking: M12 A, B, C, D and P-coding
- IEC 61076-2-109 M12 connectors with screw-locking for data transmission frequencies up to 500 MHz: M12 X and H-coding
M12 Power Connector Standards:
- IEC 61076-2-111 M12 power connectors with screw-locking: M12 E, F, K, L, M, S, T-coding
- IEC 61076-2-113 M12 connectors with screw-locking, power and signal contacts for data transmission frequencies up to 100 MHz: M12 Y-coding
While both fall under the broader IEC 61076-2 series, M8 and M12 connectors are governed by different specific standards within this series. M8 connectors are addressed by standards, including IEC 61076-2-104 and IEC 61076-2-114. M12 connectors, due to their wider range of applications and configurations, are covered by a more extensive set of standards, including IEC 61076-2-101, IEC 61076-2-109, IEC 61076-2-111, and IEC 61076-2-113.
Electrical Performance
The most significant distinction in the electrical characteristics of M8 and M12 connectors is their rated voltage and rated current.
- Rated Voltage: M12 connectors typically have higher voltage ratings (e.g., 250V or higher) compared to M8 connectors (e.g., 60V or less).
- Rated Current: Similarly, M12 connectors can handle higher currents (e.g., 4A or more) than M8 connectors (e.g., 3A or less).
The following table compares the rated voltage and rated current specifications of M8 and M12 connectors.
| M8 Connectors | M12 Connectors | |
|---|---|---|
| Rated Voltage: | 60V for 3/4/5/6 pin, 30V for 8 pin | 250V for 3/4 pin, 60V for 5/6pin, 30V for 8/12/17 pin |
| Rated Current: | 4A for 3/4/5 pin, 2A for 6 pin, 1.5A for 8 pin | 4A for 3/4/5/6 pin, 2A for 8pin, 1.5A for 12/17 pin |
Application Areas:
M8 connectors are best suited for space-constrained applications with lower power and signal requirements, while M12 connectors are preferred for more demanding applications requiring higher performance, robustness, and support for industrial communication protocols.
Common Applications of M8 Connectors:
M8 connectors, due to their compact size, are typically found in applications with limited space or where miniaturization is a key design consideration. Common examples include:
- Small Sensors and Actuators: Proximity sensors, photoelectric sensors, pressure sensors, and small actuators often use M8 connectors for their compact size and reliable connection.
- Robotics in Confined Spaces: On robotic arms, grippers, and other robotic systems operating in tight spaces, M8 connectors minimize weight and space requirements.
- Miniature Devices and Equipment: Small industrial cameras, measuring instruments, and other compact devices often utilize M8 connectors.
- Automation in Electronics Manufacturing: In the production of electronic components and devices, where precision and miniaturization are essential, M8 connectors are commonly used.
- Material Handling Systems: Used in conveyor systems, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and other material handling equipment for connecting sensors and actuators.
Common Applications of M12 Connectors:
M12 connectors, with their greater robustness, higher pin counts, and better electrical performance, are typically used in more demanding applications:
- Industrial Automation and Control Systems: Connecting sensors, actuators, I/O modules, and other devices in complex automation systems.
- Robotics and Automation in Harsh Environments: In robotic applications exposed to harsh conditions like welding, machining, or outdoor environments, M12 connectors provide reliable connections.
- Fieldbus and Industrial Ethernet Networks: M12 connectors with appropriate codings (D-coding for Ethernet, B-coding for PROFIBUS, X-coding for high-speed Ethernet) are the standard choice for industrial communication networks.
- Heavy-Duty Machinery and Equipment: Connecting sensors, actuators, and power supplies in heavy machinery, construction equipment, and other demanding applications.
- Food and Beverage Industry: In applications requiring frequent washdowns and strict hygiene standards, M12 connectors with appropriate IP ratings (e.g., IP69K) and materials (e.g., stainless steel) are used.
- Transportation (Rail, Automotive): Used in various transportation applications for connecting sensors, actuators, and communication systems.

Cost
Generally, M8 connectors are more cost-effective than M12 connectors due to their smaller size and simpler design. However, the overall system cost should be considered, as using a less suitable connector may lead to performance issues or failures, ultimately increasing costs.
The following table highlights the key distinctions between M8 and M12 connectors.
| M8 Connectors | M12 Connectors | |
|---|---|---|
| Interface Size | 8mm | 12mm |
| Thread Specifications | M8x1 | M12x1 |
| Codings | A, B, D | A, B, C, D, X, S, T, K, L, M |
| Number of Pins | 3, 4, 5, 6, 8 | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 12, 17 |
| Standards | IEC 61076-2-104, IEC 61076-2-114 | IEC 61076-2-101, IEC 61076-2-109, IEC 61076-2-111, IEC 61076-2-113 |
| Rated Voltage | 30-60V | 30-250V |
| Rated Current: | 1.5-4A | 1.5-4A |
Metabee is a leading manufacturer of M-series circular connectors. We offer a comprehensive range of high-performance, cost-effective M12 and M8 connectors. Furthermore, we provide custom design and manufacturing services to fulfill your unique application needs. Contact us to discuss your requirements.
Similarities Between M8 and M12 Connectors
While the previous section highlighted the key differences, it’s equally important to recognize the shared characteristics that make M8 and M12 connectors suitable for industrial applications.
Coupling Method and Locking Mechanism
Both M8 and M12 connectors utilize a threaded coupling mechanism for secure and reliable mating. This screw-locking system ensures a strong connection that resists accidental disconnection due to vibration, shock, or pulling forces. The thread also provides a degree of sealing when properly tightened.
Despite the secure locking mechanism, both M8 and M12 connectors are designed for relatively easy connection and disconnection. This is important for maintenance, troubleshooting, and system modifications.
Materials and Construction
Metabee M8 and M12 connectors are typically constructed from durable materials designed to withstand harsh industrial conditions. Common materials include:
- Metal Shells & Housings: Often made of nickel-plated brass or stainless steel for robust protection against mechanical stress, corrosion, and electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Plastic Housings: Typically made of durable engineering plastics that offer good chemical resistance and electrical insulation.
- Contacts: Commonly made of copper alloys with gold plating to ensure good conductivity and corrosion resistance.
The materials and plating of M8 and M12 connectors are shown in the table below.
| Materials | Plating | |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Shells | Brass or stainless steel | Nickel-plated |
| Plastic Housings | Plastics | None |
| Contact | Copper alloy | Gold-plated |
Netabee M8 and M12 connectors are designed for robust construction, able to withstand vibration, shock, and temperature fluctuations commonly found in industrial settings.
Protection Rating (IP Rating)
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating defines the level of protection against solid objects (dust, dirt) and liquids (water). Both M8 and M12 connectors commonly offer IP67 and IP68 ratings.
- IP67: Protected against dust and immersion in water up to 1 meter for up to 30 minutes.
- IP68: Protected against dust and immersion in water more than 1 meter for long periods.
This high level of protection makes them suitable for use in demanding industrial environments where exposure to dust, moisture, and other contaminants is common.
Applications
M8 and M12 connectors share some common application areas:
- Sensor and Actuator Connections: Both are extensively used for connecting sensors and actuators in various industrial automation applications.
- Industrial Environments: Both are designed for use in harsh industrial environments with exposure to dust, moisture, vibration, and temperature fluctuations.
- Automation and Control: Both play a crucial role in enabling automation and control in various industries.
Operating Temperature Range
Both M8 and M12 connectors are designed to operate within a broad temperature range suitable for most industrial environments. Typically, this range is between -25°C to +85°C.
Choosing Between M8 and M12: Application Scenarios and Recommendations
Selecting the right connector is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in any application. While M8 and M12 connectors share many similarities, their distinct characteristics make them better suited for different scenarios. This section provides detailed application examples and recommendations to help you make the right choice.
Factors to Consider:
Before selecting, let’s recap the key factors that influence connector selection:
- Space Constraints: This is often the primary factor. If space is limited, M8 is the obvious choice.
- Electrical Requirements (Voltage and Current): Higher power demands necessitate M12 connectors due to their superior current-carrying capacity and voltage ratings.
- Signal Complexity (Number of Signals): If multiple signals or data lines need to be transmitted, M12 connectors with higher pin counts offer more flexibility.
- Environmental Conditions: Harsh environments requiring high IP ratings are suitable for both, but the specific IP rating (IP67 or IP68) and material selection should be carefully considered.
- Mechanical Stress (Vibration, Shock): While both are robust, M12 connectors generally offer greater resistance to mechanical stress due to their larger size and more robust construction.
- Cost: M8 connectors are generally more cost-effective, but the overall system cost, including potential downtime and maintenance, should be considered.
- Future Expansion: If future expansion or upgrades are anticipated, choosing M12 from the outset might be a better long-term investment due to its greater versatility.

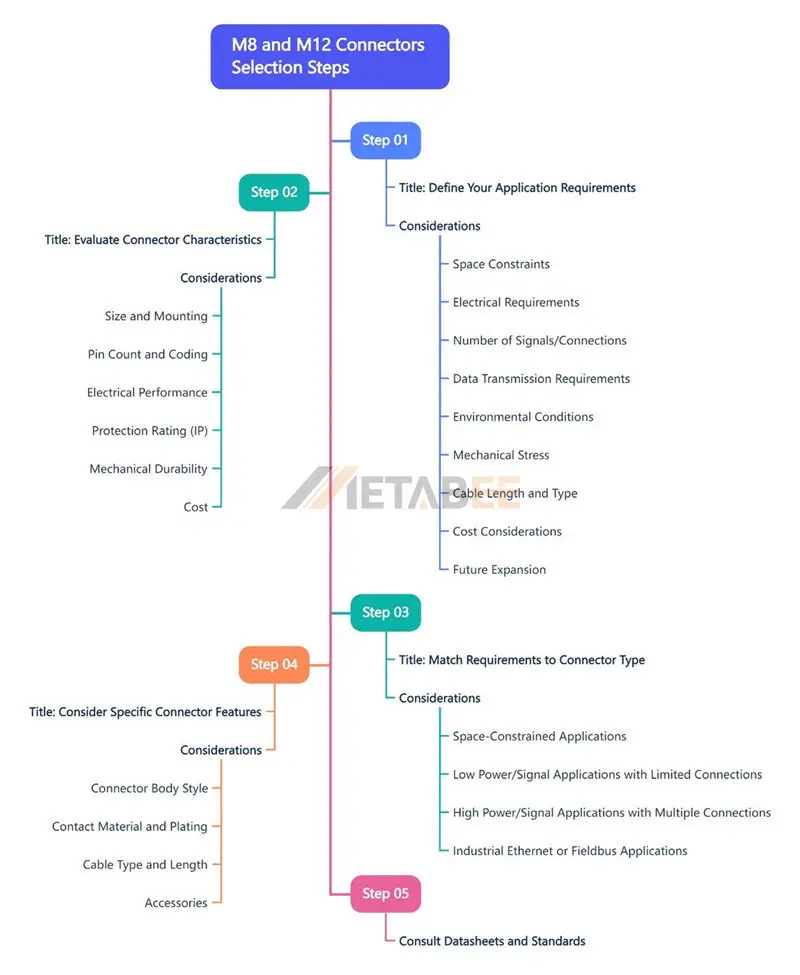
Selection Guide for M8 and M12 Connectors
Step 1: Define Your Application Requirements
Before considering connector types, clearly define your application’s needs:
- Space Constraints: How much space is available for connector installation? Are there any size restrictions?
- Electrical Requirements: What are the voltage and current requirements? Are there any specific power or signal integrity needs?
- Number of Signals/Connections: How many signals or connections need to be transmitted? This will determine the required pin count.
- Data Transmission Requirements: Is high-speed data transmission required (e.g., Ethernet)? If so, what bandwidth is needed?
- Environmental Conditions: What are the operating environment’s conditions? Are there exposure to dust, water, chemicals, extreme temperatures, or vibrations?
- Mechanical Stress: Will the connector be subjected to vibration, shock, or other mechanical stresses?
- Cable Length and Type: What cable length is required? What type of cable is needed (e.g., shielded, flexible)?
- Cost Considerations: What is the budget for the project? While M8 is generally cheaper, consider the total cost of ownership, including potential maintenance and downtime.
- Future Expansion: Are there plans for future expansion or upgrades? Choosing a more versatile connector (like M12) might be beneficial in the long run.
Step 2: Evaluate Connector Characteristics
Now, you should consider the key characteristics of M8 and M12 connectors:
- Size and Mounting: M8 is smaller (8mm thread), ideal for tight spaces. M12 is larger (12mm thread), offering greater robustness and more space for connections.
- Pin Count and Coding: M8 typically offers 3-8 pins, while M12 can have up to 17. Coding prevents mismating; choose the appropriate coding (A, B, D, X, S, T) based on the application.
- Electrical Performance: M12 generally handles higher voltage and current than M8. Consult datasheets for specific ratings.
- Protection Rating (IP): Both offer excellent protection (IP67/68). Choose the appropriate rating based on the environmental conditions.
- Mechanical Durability: M12 tends to be more robust against mechanical stress due to its larger size.
- Cost: M8 is generally more cost-effective.
Step 3: Match Requirements to Connector Type
Based on the information gathered in steps 1 and 2, match your application requirements to the appropriate connector type.
- Space-Constrained Applications: If space is a primary concern, M8 is the preferred choice.
- Low Power/Signal Applications with Limited Connections: M8 is suitable for simple sensor and actuator connections with low power and signal requirements.
- High Power/Signal Applications with Multiple Connections: M12 is necessary for applications requiring higher power, multiple signals, or high-speed data transmission.
- Harsh Environments with High Mechanical Stress: M12 is generally preferred for its increased robustness and resistance to mechanical stress.
- Industrial Ethernet or Fieldbus Applications: M12 with appropriate coding (D, X, B) is the standard choice.
Step 4: Consider Specific Connector Features
Once you’ve chosen between M8 and M12, consider specific connector features:
- Connector Body Style: Straight, angled, or panel mount.
- Contact Material and Plating: Choose appropriate materials for corrosion resistance and conductivity.
- Cable Type and Length: Select cables that match the application requirements and connector type.
- Accessories: Consider using accessories like cable glands, sealing caps, and mounting hardware.
Step 5: Consult Datasheets and Standards
Always consult the manufacturer’s datasheets for detailed specifications and ratings. Ensure the chosen connector complies with relevant industry standards.
Download Metabee’s M Series Connector Catalog (PDF format, 3.6Mb)
By following these steps, you can confidently select the appropriate M8 or M12 connector for your application, ensuring reliable and efficient performance.
If you remain uncertain about the optimal choice between an M8 and M12 connector for your specific application, our technical team is ready to provide expert guidance. Please feel free to reach out to us for tailored recommendations.
Application Scenarios and Recommendations
Here are some specific application scenarios and recommendations:
- Small Sensors and Actuators: M8 connectors are typically the ideal choice due to their compact size and sufficient electrical performance for these applications.
- Robotics in Confined Spaces: M8 connectors are often preferred to minimize weight and space requirements on the robot.
- Machine Vision Systems: Both M8 and M12 can be used depending on the specific requirements. M12 is often chosen for higher-resolution cameras requiring more data bandwidth.
- Industrial Ethernet Networks: M12 connectors with D-coding or X-coding are the standard choice for industrial Ethernet due to their higher bandwidth capabilities and robust shielding.
- Fieldbus Systems (e.g., PROFIBUS): M12 connectors with B-coding are typically used for PROFIBUS applications.
- Heavy-Duty Machinery and Equipment: M12 connectors are generally preferred due to their higher robustness, current-carrying capacity, and resistance to mechanical stress.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Both M8 and M12 connectors with appropriate IP ratings (IP69K is often required) and materials (e.g., stainless steel) can be used. M12 might be chosen for applications requiring higher current or more complex connections.
- Outdoor Applications: Both M8 and M12 connectors with appropriate IP ratings and UV-resistant materials are suitable.

Related Products
M8 and M12 connectors are often part of a larger ecosystem of connectivity solutions. Understanding the related products can help you create complete and efficient systems. This section provides an overview of common products associated with M8 and M12 connectors.
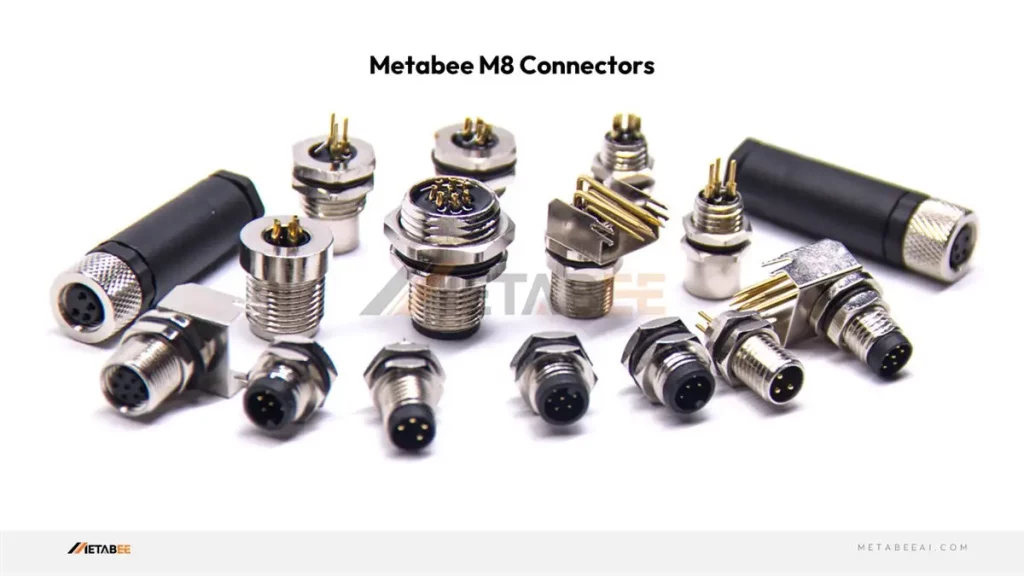
M8 Connectors
Metabee offers a wide range of M8 connectors, including field-wireable, panel mount, and PCB mount options.

M12 Connectors
Metabee offers a wide range of M12 connectors, including field-wireable, panel mount, and PCB mount options.

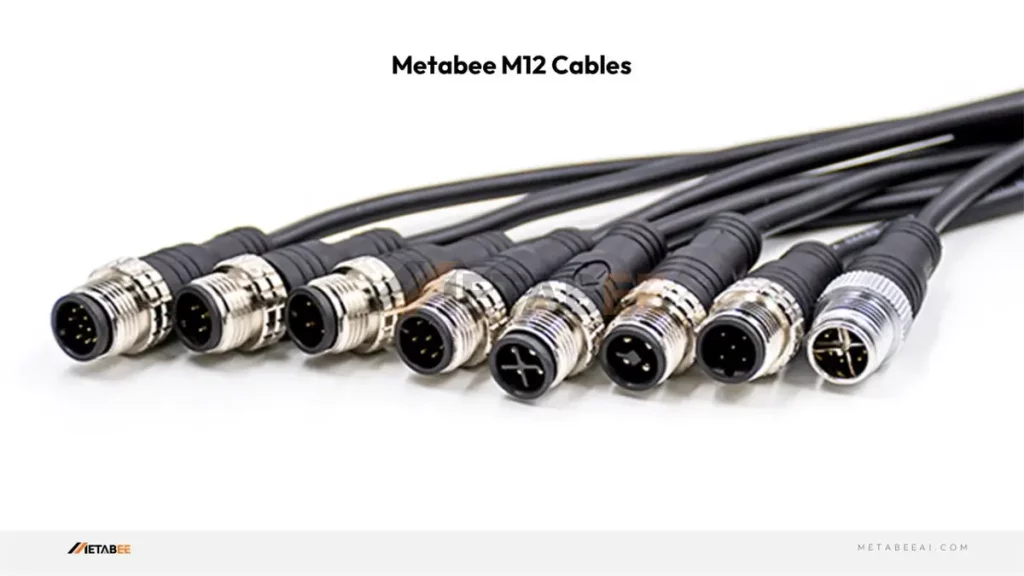
M12 Cables (Patch Cables/Adapter Cables)
Metabee M12 cables allow you to connect devices with different connector sizes.

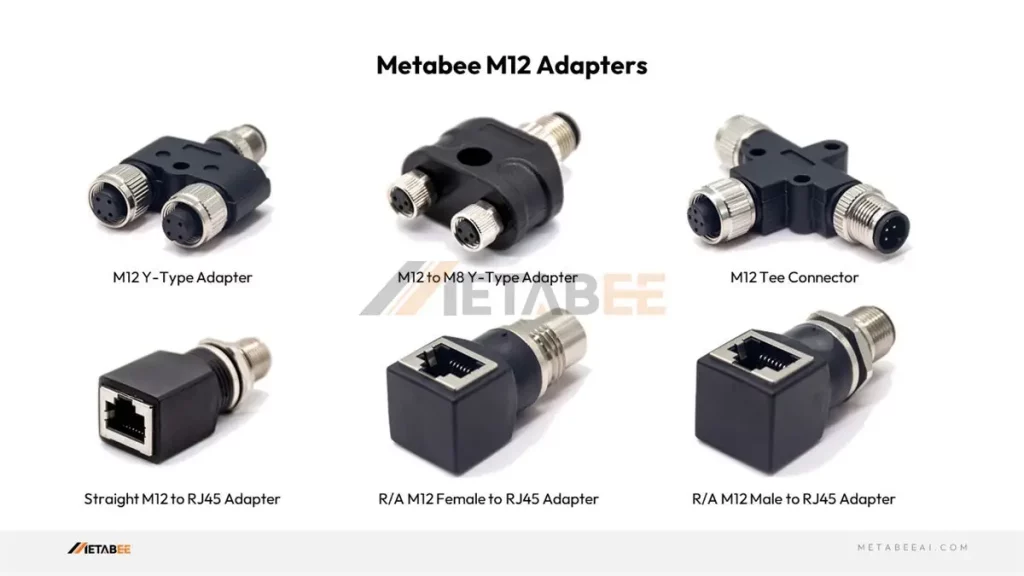
M12 Adapters
Metabee M12 adapters provide a direct connection between M12 connectors and other connectors without a cable.

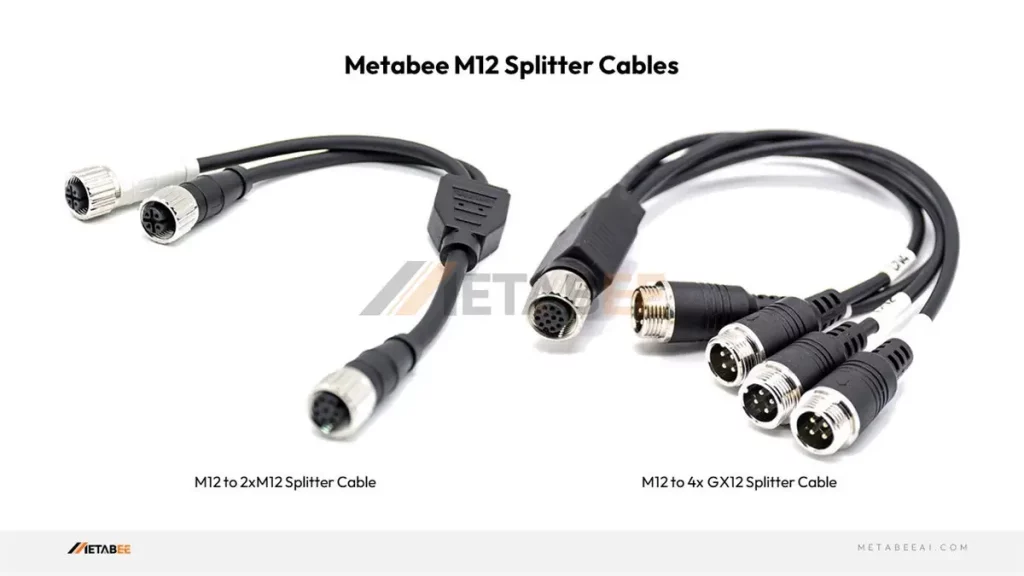
M12 Splitter Cables (Y-Cables)
Similar to M12 Tee connectors, M12 splitter cables provide a branching connection but with the flexibility of cables.

M8/M12 I/O Sensor Distribution Boxes
These I/O sensor distribution boxes provide a centralized connection point for multiple sensors and actuators.

Conclusion
In the realm of industrial automation, reliable connectivity is paramount, and M8 and M12 connectors serve as essential components for ensuring seamless data and power transmission. This guide has provided a comprehensive comparison, highlighting the key differences between these two widely used connector types. We explored their variations in size, thread specifications, coding options, pin counts, electrical performance, environmental protection, and cost. M8 connectors offer a compact and cost-effective solution for space-constrained applications with lower power and signal requirements. And M12 connectors provide enhanced robustness, higher pin counts, and superior electrical performance for more demanding applications, including industrial Ethernet and fieldbus systems.
Ultimately, selecting between M8 and M12 connectors depends on a careful evaluation of specific application needs. Factors such as space limitations, electrical requirements, signal complexity, environmental conditions, and budget should all be considered. Furthermore, understanding the range of related products, including cables, adapters, and distribution boxes, allows for the design of complete and efficient connectivity solutions. Choosing the right connector is an investment in system reliability, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity in any industrial setting.
If you have any questions or require technical assistance, please leave a comment below or contact us. Our expert technical team is ready to help.