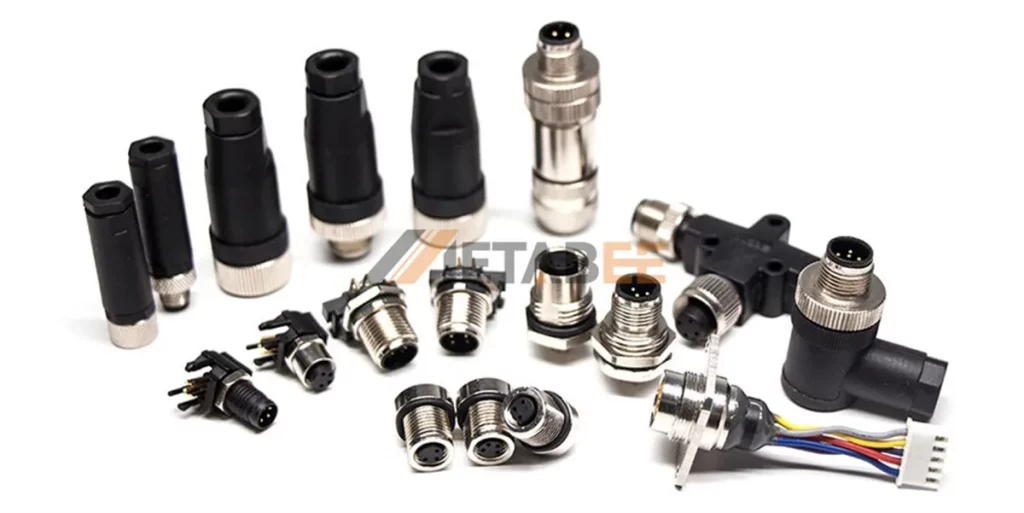
M12 connectors are an essential component of the industrial automation industry. They are the invisible heroes who keep data flowing and equipment working efficiently. However, with so many M12 connector types available, it might be difficult to determine which one to use for your application.
M12 connectors have been widely used for decades, even before the introduction of the Internet of Industrial Things (IIoT) and Industry 4.0. They transmit data from devices to applications, where it is collected and presented to the user. They connect programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, I/O blocks, and wireless access points (WAPs). These connectors can also transmit high power for long periods, making them ideal for AC motors and drives, motor control switches, and low-voltage applications like fieldbus Ethernet components and network devices.
This post will explain everything you need to know about M12 connector types. I’ll provide you with a visual summary of the various types, explain what distinguishes them, and help you confidently choose the best connector for your next project.
About M12 Connectors
M12 connectors are a kind of circular connectors with a screw-on thread diameter of 12 millimeters. This simple design provides various benefits that make it suitable for industrial automation applications.
- Durability: Their metal shell and screw-on thread offer great resistance to shock, vibration, and extreme temperatures.
- Waterproof: Many M12 connectors have an IP rating of IP67 or IP68, indicating that they are dust-tight and can be submerged in water for extended periods.
- Ease of Use: The screw-on thread provides a secure connection without needing any extra tools.
- Versatility: M12 connectors are available in a variety of configurations, including different pin counts, coding types, and mounting methods. Because of their versatility, they can be used for various applications, including data transmission and power distribution.

Related Post:
What is an M12 Connector? A Complete Overview
20 Popular Types of M12 Connector
M12 connectors may look simple, but their actual appeal is their variety. I classified M12 connectors into 20 types based on their coding, number of pins, and mount methods.
M12 Connector Types By Coding
You can consider coding as the language spoken by the M12 connectors. Each coding type, represented by a letter, indicates the type of signal that the connector can transport.
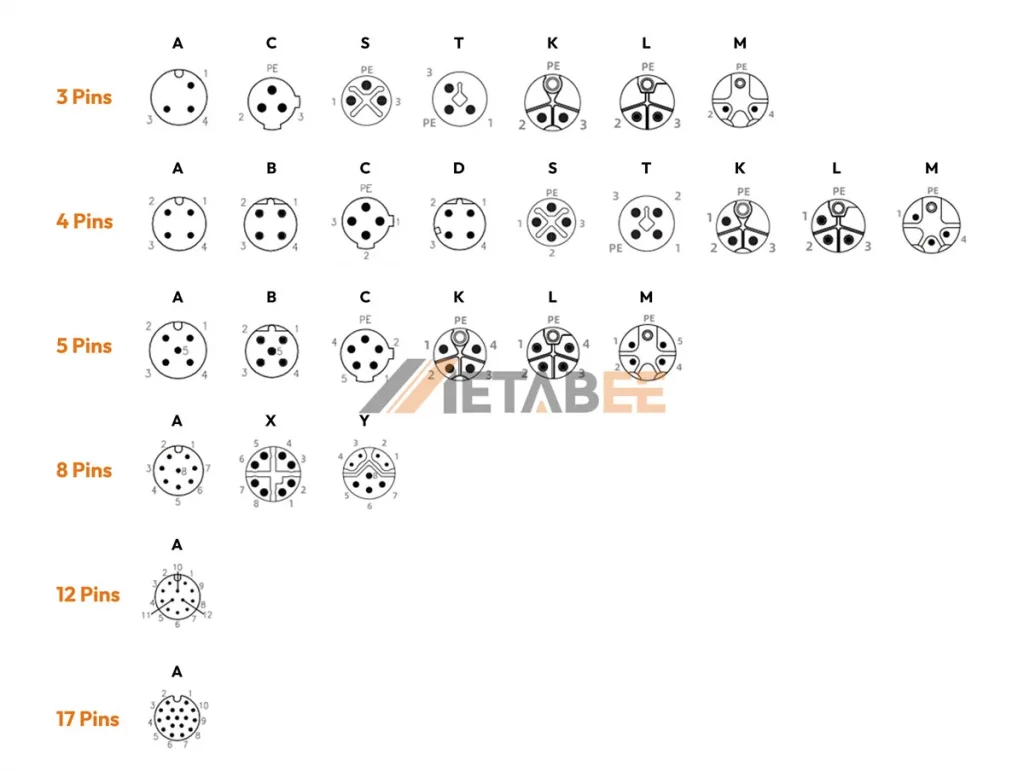
Here’s a breakdown of the most common M12 coding types:
A-coded(Universal)
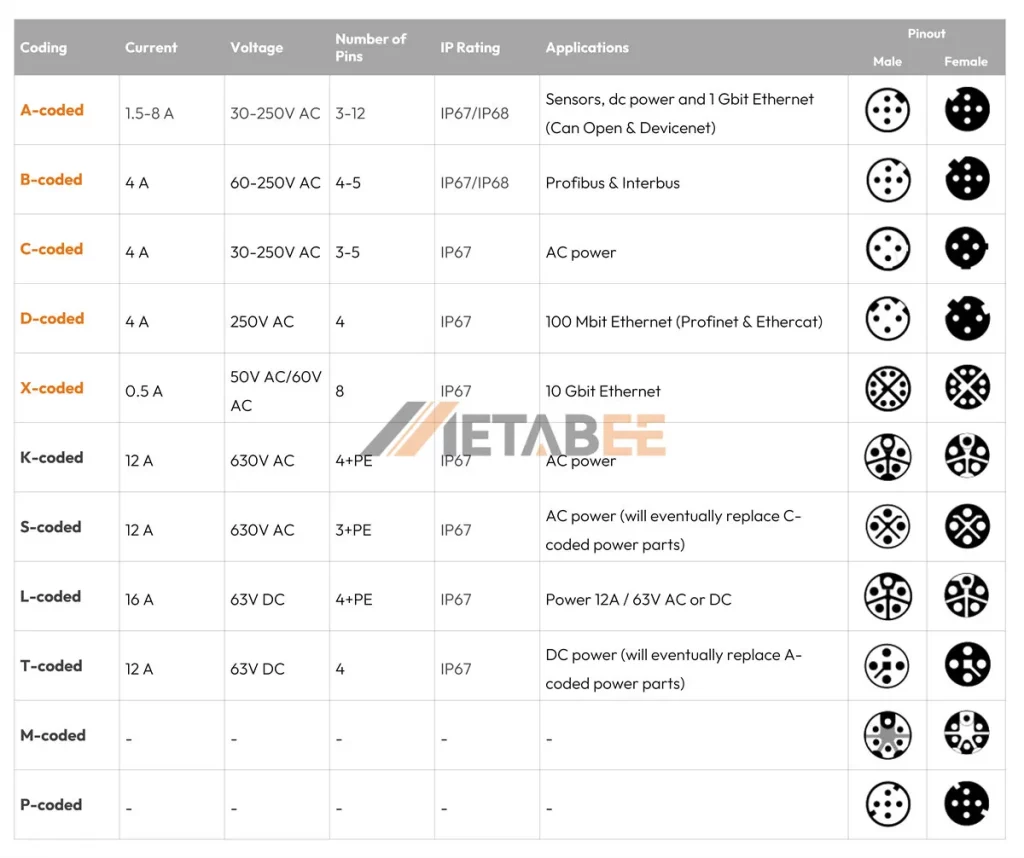
A-coded is the most widely used coding. M12 A-coded connectors are perfect for sensors, actuators, DC power, and 1 Gigabit Ethernet applications (Can Open and DeviceNet). They typically come with 3 to 17 pins, offering flexibility for various data and low-power applications.
B-coded(Networking)
M12 B-coded connectors are commonly used for Profibus and Interbus fieldbus systems. They usually have 4 or 5 pins. Besides, they have a different key to avoid unintentional mixing with A-coded connectors.
C-coded(AC Power)
M12 C-coded connectors are designed for AC power applications. You can find them on AC-powered sensors and actuators. They typically have 3 to 6 pins.
Please note that M12 S-coded connectors are emerging as a future alternative for C-coded power applications. Because they have a more compact design along with higher power-handling capabilities.
D-coded(Ethernet)
M12 D-coded connectors are currently one of the most common M12 connectors. They typically have 4 or 5 pins. They are used for connecting field devices to industrial networks. For example, the 4-pole M12 connector is becoming standard on Ethernet, ProfiNet, and EtherCat field devices. Besides, it’s always used with industrial CAT5e cables capable of transferring up to 100 Mbit/s.
If you are looking for gigabit data transfer rates and CAT6-rated connections, you will require an M12 X-coded connector (see below).
X-coded (High-speed Ethernet)
M12 X-coded connectors are designed to meet the high-speed requirements of current industrial networks. They are rapidly becoming the standard for high-speed industrial Ethernet applications. They can handle data transfer rates of up to 10 Gbit/s. The galvanic separation plates that isolate the wire pairs in the shape of an X make them easy to identify. Additionally, they usually feature 4 or 8 pins and a unique keyway design to guarantee proper connection.
While the above-mentioned coding types cover the most often encountered M12 connectors, you may find a few less common codes:
K-coded
M12 K-coded connectors are designed for transmitting AC power. They can handle higher power levels, typically up to 12 A and 630 V AC. So, they are suitable for AC motors, drives, and other high-power equipment. These connectors have 5 Pins (4+PE).
S-coded
M12 S-coded connectors, like M12 K-coded connectors, are also used for transmitting AC power. They can handle currents up to 12 A and voltages up to 630 V AC. They are available in 3-pin (2+PE) or 4-pin (3+PE) varieties.
L-coded
M12 L-coded connectors are widely used for transmitting DC power with high current. They can support currents up to 16 A and voltages up to 63 V DC, making them excellent for powering field devices such as sensors, actuators, and I/O modules. They are available in 4-pin and 5-pin (4+PE) configurations.
T-coded
M12 T-coded connectors, like L-coded connectors, are also designed for DC power connections. They can support currents up to 12 A and voltages up to 63 V DC. Compared to M12 L-coded connectors, they feature a lower current rating and have no PE option.
M-coded and P-coded
These codes are under development and intended for special purposes, such as early mate/last break contacts for critical control systems.
That’s a lot of M12 codes to handle! To help you understand and differentiate these connectors, I created a table about the coding of M12 connectors.
M12 Connector Types By Number of Pins
An M12 connector’s number of pins determines how many separate wires it can accept, similar to highway lanes. Choosing the right quantity is important for proper signal transmission or power delivery.
There are 6 popular types of M12 connectors, divided by the number of pins:
- M12 3-Pin Connectors
- M12 4-Pin Connectors
- M12 5-Pin Connectors
- M12 8-Pin Connectors
- M12 12-Pin Connectors
- M12 17-Pin Connectors
In addition to these standard pin numbers, Metabee can supply M12 connectors with unusual pin numbers such as 6-pin, 7-pin, 9-pin, 10-pin, 11-pin, and so on. Please contact our technical team if you have any questions related to M12 connectors.
M12 Connector Types By Mount Methods
Another essential question is how to mount the M12 connector. Here are 3 popular mounting types:
Cable mount
M12 cable connectors are connected directly to the end of the cables. There are 2 types of cable mounts: screw joints and soldering. M12 field wireable connectors always have a screw joint termination.
Panel mount
M12 panel mount connectors are suitable for mounting on a panel or enclosure. There are two kinds of panel mounts: bulkheads and 4-hole flanges.
PCB through-hole mount
M12 PCB connectors always have a through-hole mount termination.

How to Choose the Right M12 Connector for Your Applications?
M12 connectors offer a wide range of options, but with great versatility comes the responsibility to choose the right one. There are 5 key factors you should consider when choosing M12 connectors.
Decide the coding type
What type of signal are you dealing with? Is it data transmission (Ethernet), sensor signals, power delivery, or something else entirely? Understanding the application will lead you toward the correct coding type (A-coded, D-coded, etc.).
Decide the number of pins
Once you know the coding, you should figure out how many wires or signals you need to transmit. This determines the number of pins required on the connector. For example, a basic sensor connection may only require 3 pins (A-coded), whereas a high-speed Ethernet application may require an X-coded connector with 8 pins.
Consider the mounting type
You should consider how to mount this connector. Panel mount connectors are appropriate for permanent installation on control panels, whereas cable mount connectors provide greater flexibility when connecting remote equipment. Besides, field-attachable connectors are useful for on-site repairs and custom configurations.
Consider the environment
Industrial environments can be severe. Will your connector be exposed to dust, water, or high temperatures? You should ensure that the M12 connector has the correct IP rating for your environment.
Choose materials
Typically, the materials of M12 connectors are nickel-plated brass or stainless steel. Brass is a cost-effective option for most applications, while stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance for demanding environments.
By following these steps, you can easily select the correct M12 connector for your applications. If you are still unclear, please do not hesitate to contact us for assistance; our professionals would be pleased to help you.
After all, choosing the right M12 connector ensures a smooth-running and reliable industrial automation system.
Applications
M12 connectors are the hidden heroes of many industrial automation systems. Their adaptability and dependability make them essential components in keeping factories, power plants, and other industrial facilities running smoothly. Here’s a look at some of the popular applications where M12 connectors play a key role:
Sensor Connections:
Sensors are vital components of industrial automation, providing real-time data on temperature, pressure, flow, and other crucial parameters. M12 connectors, particularly A-coded versions with 3 or 4 pins, are commonly utilized to link these sensors to controllers and data-collecting systems.
Actuator Control:
Actuators convert electrical signals into physical movements that control valves, robots, and other automated equipment. M12 connectors, again A-coded, guarantee dependable signal transfer to control these actuators, allowing industrial operations to run smoothly.
Industrial Ethernet:
Ethernet networks are the foundation of modern industrial communication, connecting devices and systems throughout a facility. D-coded M12 connectors, with 4 or 8 pins, are suitable for 100 Mbit Ethernet connections in Profibus and EtherCAT networks. Besides, X-coded M12 connectors are gaining popularity for high-speed Gigabit Ethernet applications.
Fieldbus Systems:
B-coded M12 connectors are commonly used in specialized industrial networks such as Profibus and Interbus. These connectors, which typically have 3 to 5 pins, allow communication between various devices on these fieldbus networks.
Power Supplies:
While A-coded M12 connectors can be used in DC power applications, M12 C-coded connectors are primarily designed for AC power supply. They are commonly used with AC motors, drives, and other industrial equipment. You should keep a lookout for new M12 S-coded connectors. They have the potential to replace C-coded power applications in the future.
Beyond Industrial Automation:
M12 connectors’ versatility extends beyond traditional industrial applications. They are currently utilized in alternative energy applications like solar and wind farms to connect sensors, controllers, and data-collecting systems. Their durability and weather resistance make them perfect for use in challenging environments.

Conclusion
M12 connectors are not just common electrical connectors; they are the hidden heroes of industrial automation. Their combination of durability, water resistance, ease of use, and versatility makes them a dependable partner for various applications.
In this article, I categorized M12 connectors into 20 types according to their coding, number of pins, and mounting methods. Understanding these types can help you make better choices. Finally, I’ve described the best method for choosing M12 connectors based on my experience. In addition, I’ve included popular applications for M12 connectors to assist you in making better decisions.
If you have any questions related to M12 connectors, please leave a message below or contact us directly. we are pleased to help you.
Pingback: M8 vs M12 Connector: Everything You Need to Know - MetabeeAI
Pingback: A Practical Guide to Selecting M12 Connectors with Confidence - connector manufacturer
Pingback: Upgrade Your Industrial Network with the Right M12 Connector - connector manufacturer
Pingback: How to Identify M12 5-Pin Connector Pinouts in 2025 - connector manufacturer
Pingback: Are 8-Pin M12 Connectors Right for Your Next Project - connector manufacturer
Pingback: The Ultimate Guide to M12 Connector Pinout and Wiring Diagram - MetabeeAI