In RF technology, TNC coaxial connectors are known for their durable design, secure threaded coupling, and ability to perform well at high frequencies. These features make them essential components in various industries, ensuring reliable connections. This post will empower you with a solid understanding of TNC connectors, covering their history, design, specifications, applications, and comparison with other RF connector types.
- What is a TNC Connector?
- 9 Common TNC Connector Types
- TNC Connector Dimensions
- TNC Connectors Specifications
- Applications of TNC Connectors
- BNC vs TNC vs RP-TNC Connectors
- How to Choose the Right TNC Connectors?
- The Main TNC Connector Manufacturers
- TNC Adapters and Cable Assemblies
- Conclusion
- Related Products
What is a TNC Connector?
The TNC coaxial connector is a threaded RF connectors that provide secure and reliable connections for coaxial cables, ensuring superior performance even in high-vibration environments.

Definition
TNC connector (Threaded Neill-Concelman) is a robust evolution of BNC connectors. Designed for demanding RF applications, their threaded coupling ensures a more secure, stable connection in harsh environments.
History
Since their invention by Paul Neill and Carl Concelman in the late 1950s, TNC connectors have found extensive application. Their durable construction and wide frequency range made them a versatile choice for various applications. Their enduring relevance highlights their significance in the field.
Standard
IEC61169-17
IEC61169-17 is the most specific standard for TNC connectors from the International Electrotechnical Commission. It details the dimensions, interface requirements, and performance characteristics.
This includes:
- Mechanical dimensions: Defines the connector body’s precise dimensions (the outer conductor’s inner diameter is 6.5 mm (0.256 in)), threads, and mating interfaces to ensure compatibility between different manufacturers.
- Electrical characteristics: Specifies impedance (typically 50 ohms), frequency range, work voltage, and other electrical parameters.
- Environmental performance: Outlines tests and requirements for temperature range, corrosion resistance, and vibration resistance.
MIL-STD-348
The interface specifications of the TNC connector are defined in MIL-STD-348, a United States military standard that outlines the standard dimensions and configurations for various RF coaxial connectors.
Design Mechanism and Materials
TNC connectors use threaded coupling to prevent accidental disconnection and minimize signal loss. They use brass, with nickel or gold plated for corrosion resistance, and feature the Teflon insulator to maintain signal integrity.
Main Materials of TNC Connectors:
| Component | Material |
|---|---|
| Shell/Body | Brass |
| Contact | Brass |
| Insulator | TEFLON |
Benefits
TNC connectors have many benefits, making them a main choice over other connectors.
Stable Connection.
The TNC connectors use a threaded coupling design, which provides a robust and stable connection, reducing the risk of signal loss or disconnection.
High-Frequency Performance.
The frequency range of TNC connectors is typically DC to 6 GHz. Some high-performance TNC connectors may be able to handle even higher frequencies.
Durability.
TNC connectors are made of robust brass and can withstand harsh environments, such as extreme temperatures and moisture.
Versatility.
TNC connectors have several connector styles, such as straight, right-angle, cable-type, and panel mount. They are used in most applications.
9 Common TNC Connector Types
TNC can be classified into 9 types according to polarity and gender, mounting method, and orientation.
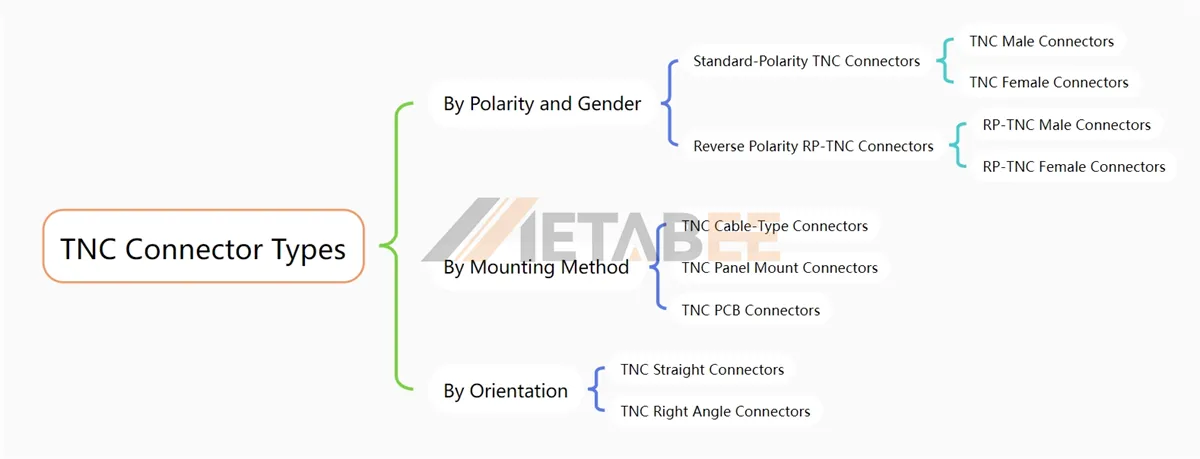
By Polarity and Gender
Standard-Polarity TNC Connectors
This is the most common type; standard TNC connectors are available in male and female configurations.
- TNC Male Connectors: These connectors have an inter-threaded and a center pin.
- TNC Female Connectors: They have an outer threaded and a center receptacle.
Reverse Polarity RP-TNC Connectors
RP-TNC connectors are a variation of the standard TNC connectors. They feature a reversed gender center contact, making them suitable for specific applications such as Wi-Fi antennas and wireless routers.
- RP-TNC Male Connectors: These connectors have an inter-threaded and a center receptacle.
- RP-TNC Female Connectors: They have an outside threaded and a center pin.

By Mounting Method
- TNC Cable-Type Connectors: These connectors can attach coaxial cables, providing a secure connection for signal transmission. According to the contact termination, they can be categorized into TNC solder, crimp, clamp, and twist-on connectors.
- TNC Panel Mount Connectors: These connectors are made for panel mounting, so they have a threaded body and a nut for secure fastening. Based on the mount feature, they can be categorized into TNC bulkhead and 4-hole flange connectors.
- TNC PCB Connectors: They are designed for direct mounting onto printed circuit boards (PCB). There is a TNC PCB through-hole type.

By Orientation
- TNC Straight Connectors: They have a straight body, with the cable or mating connector extending in the same direction.
- TNC Right Angle Connectors: These are a 90-degree bend in the body, allowing for connections at right angles. They can be useful in tight spaces or where cable routing requires a bend.

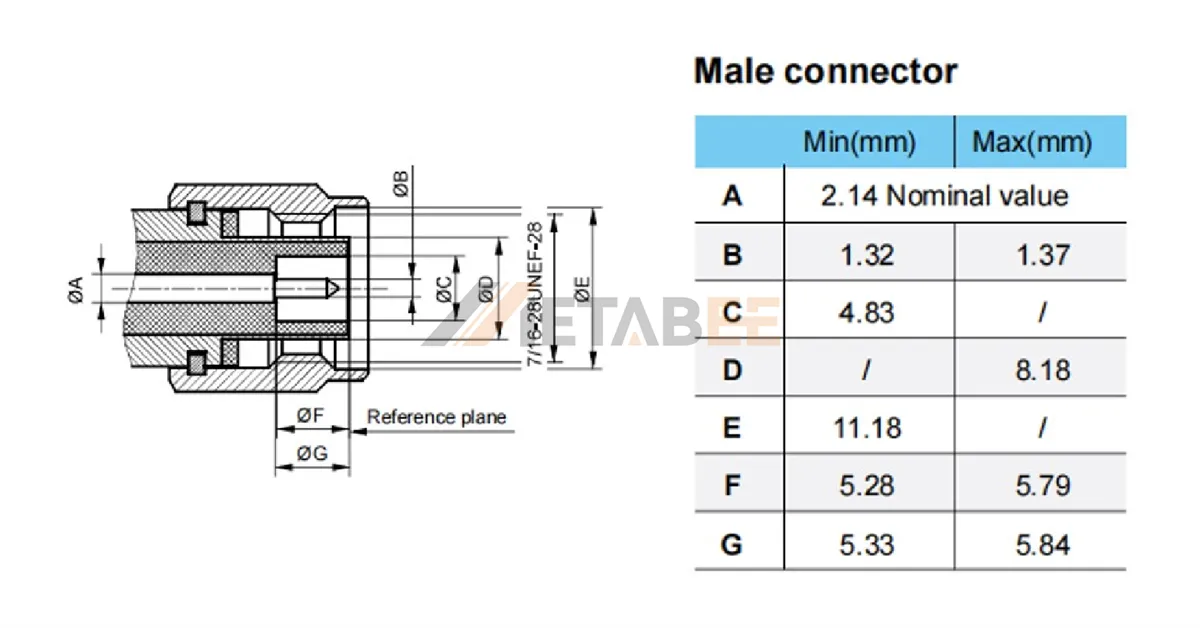
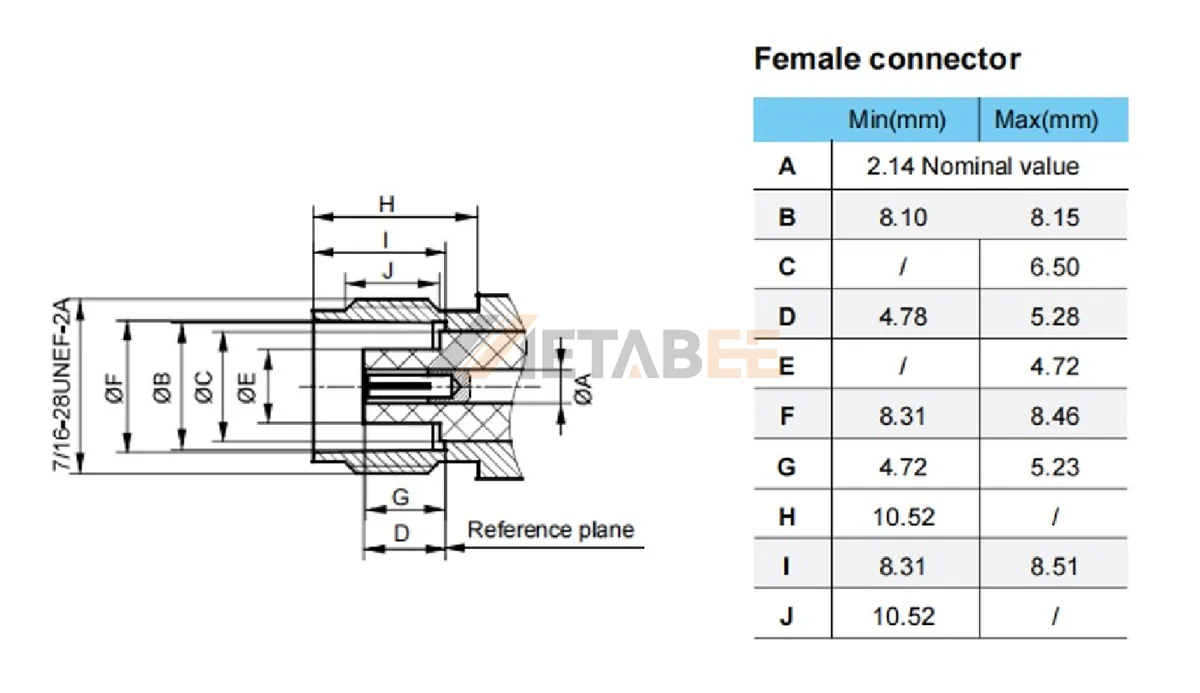
TNC Connector Dimensions
To guarantee compatibility between different manufacturers, TNC connectors use standardized interface dimensions.
Interface Diameter:
The standard thread size for TNC connectors is 7/16-28 UNEF. This means the thread has a 7/16-inch diameter and 28 threads per inch. The inner diameter of the outer conductor is 6.5 mm (0.256 in), providing a secure and vibration-resistant connection.
These standardized dimensions follow MIL-STD-348 and ensure that TNC connectors provide reliable performance across various applications.
Interface Dimensions of TNC Male/Plug Connector
Interface Dimensions of TNC Female/Jack Connector:
TNC Connectors Specifications
Due to their reliable performance, TNC coaxial connectors are a popular choice for diverse applications.
To ensure you select the right connector, it’s crucial to understand their specifications. Below are the key specifications:
Electrical Performance
Electrical performance dictates how well the connector transmits signals. Key parameters include:
- Impedance: TNC connectors are typically designed for 50 Ohm and 75 Ohm, matching common transmission lines for optimal power transfer and minimal signal reflection.
- Frequency Range: TNC connectors are capable of handling frequencies from 0 to 6 GHz or higher, depending on the specific design and application.
- VSWR: Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) is a critical parameter affecting signal integrity. TNC connectors maintain a low VSWR≤1.3:1; there are straight type≤1.3 MAX and right-angle type≤1.5 MAX, ensuring minimal signal reflection and optimal transmission efficiency.
- Dielectric Withstanding Voltage: This specifies the maximum voltage the connector can withstand without dielectric breakdown. It is rated for 1500 V RMS.
- Working Voltage: This is the maximum voltage the connector is designed to operate at continuously. It is lower than the dielectric withstanding voltage. It is rated for 500 V RMS.
Key Parameters of Electrical Performance:
| Impedance | 50 Ohm |
| Frequency Range | DC to 6 GHz |
| VSWR | Straight Type ≤1.3MAX, Right-Angle type ≤1.5MAX |
| Dielectric Withstanding Voltage | 1500 V RMS |
| Working Voltage | 500 V RMS |
| Center Contact Resistance | ≤ 3.0 mΩ Max |
| Outer Contact Resistance | ≤ 2.0 mΩ Max |
| Insulation Resistance | ≥ 5 × 103 MΩ (Megohms MIN.) |
Mechanical Performance
Mechanical specifications relate to the physical properties and robustness of the connector:
- Coupling: TNC connectors utilize a threaded coupling mechanism (7/16-28 thread) for secure and reliable connections, resisting vibration and accidental disconnection.
- Contact Retention: This measures the force required to dislodge the connector’s contacts, ensuring a stable connection even under stress. It is rated for 6 lbs MIN.
- Durability: This indicates the number of mating and unmating cycles the connector can withstand before its performance degrades. It is rated for over 500 mating cycles.
Key Parameters of Mechanical Performance:
| Coupling | 7/16-28 Threaded |
| Contact Retention | 6 lbs MIN |
| Durability | ≥ 500 Cycles |
Environmental Performance
- Temperature Range: TNC connectors operate within a broad temperature range of -5°C to +165°C.
- Nut Locking Retention: This measures the torque required to loosen the connector’s nut, ensuring the connection remains secure. It is rated for 100 lbs. MIN.
- Vibration: TNC connectors are engineered to resist mechanical vibrations, complying with MIL-STD-202 testing standards.
- Corrosion resistance: TNC connectors are often made with materials that resist corrosion, ensuring reliable performance in humid or corrosive environments. Salt spray testing is a common method for evaluating corrosion resistance.
Key Parameters of Environmental Performance:
| Temperature Range | -5°C to +165°C |
| Nut Locking Retention | 100 lbs. MIN. |
| Vibration | MIL-STD-202 Meth. 204 |
| Corrosion Resistance | MIL-STD-202 Meth. 101 |
Applications of TNC Connectors
Because of their robust construction and reliable performance, TNC connectors are widely used across diverse industries. Here are some of the key applications of TNC connectors:
Telecommunications
Cellular base stations, microwave communication systems, and satellite communications rely on TNC connectors for secure and stable connections.
Aerospace and Defense
Aerospace and defense applications are indispensable for TNC connectors due to their ability to withstand harsh environments and vibrations. They are used in radar systems, avionics equipment, and military communication devices.
Medical
Medical also is an application of TNC connectors, such as MRI machines, ultrasound equipment, and other high-frequency signal transmission equipment. They provide a safe and reliable connection, ensuring accurate results every time they are used.
Broadcasting
They are used in equipment that requires secure, high-frequency connections in broadcasting, such as microwave transmitters and receivers.

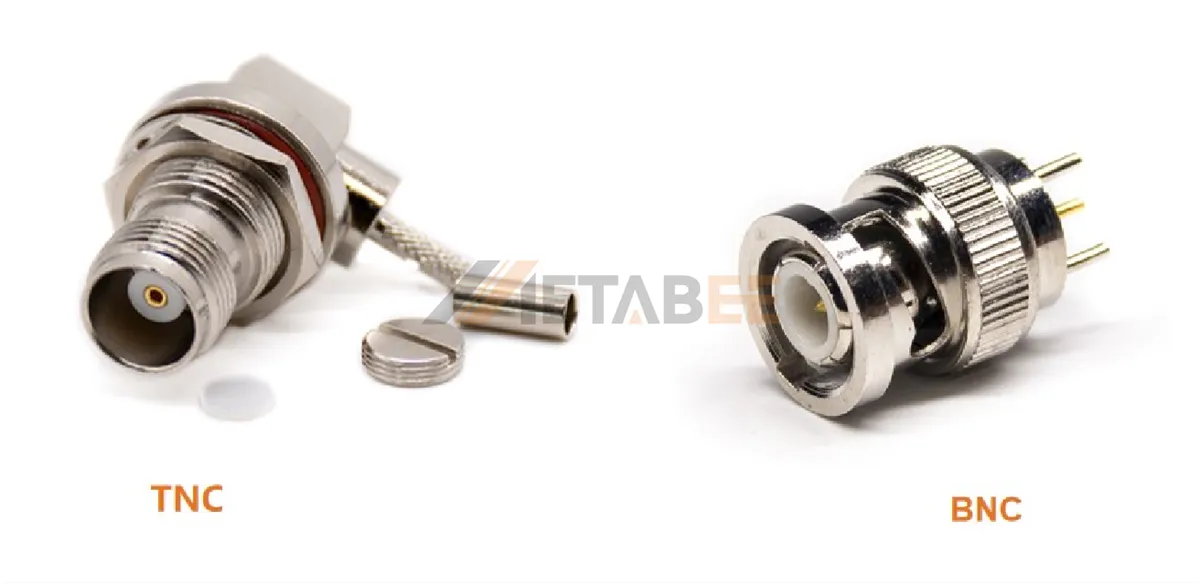
BNC vs TNC vs RP-TNC Connectors
When selecting the right connector for your application, it is important to learn about the differences between TNC connectors and other types of RF connectors. This section will compare TNC connectors with BNC and RP-TNC connectors.
BNC vs TNC Connectors
BNC connector and TNC connector both are common connector types in RF connectors.
Here’s a detailed comparison of BNC vs TNC connectors, highlighting the key differences between them.
| Feature | BNC Connector | TNC Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Bayonet Neill – Concelman | Threaded Neill–Concelman |
| Fastening Type | Bayonet coupling | Threaded coupling (screw-on) |
| Frequency Range | Typically DC to 4 GHz | Typically DC to 6 GHz |
| Main Materials | Body copper with nickel-plated Contact copper with gold-plated | Body brass with nickel-plated Contact brass with gold-plated |
| Size | Smaller, compact design | Slightly larger than BNC connectors |
| Price | More affordable | More expensive due to higher durability |
The main similarities between the two connectors are as follows:
| Feature | BNC Connector | TNC Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Connector | Coaxial RF connector | |
| Impedance | 50 Ohm or 75 Ohm | |
| Mounting | Available in cable-type, panel-mount, pcb-mount versions | |
| Insulator Materials | TEFLON | |
| IP Rating | IP65 | |
| Durability | Resistant to vibration and environmental factors | |
| Application | Used in RF systems, telecommunications, and test equipment | |

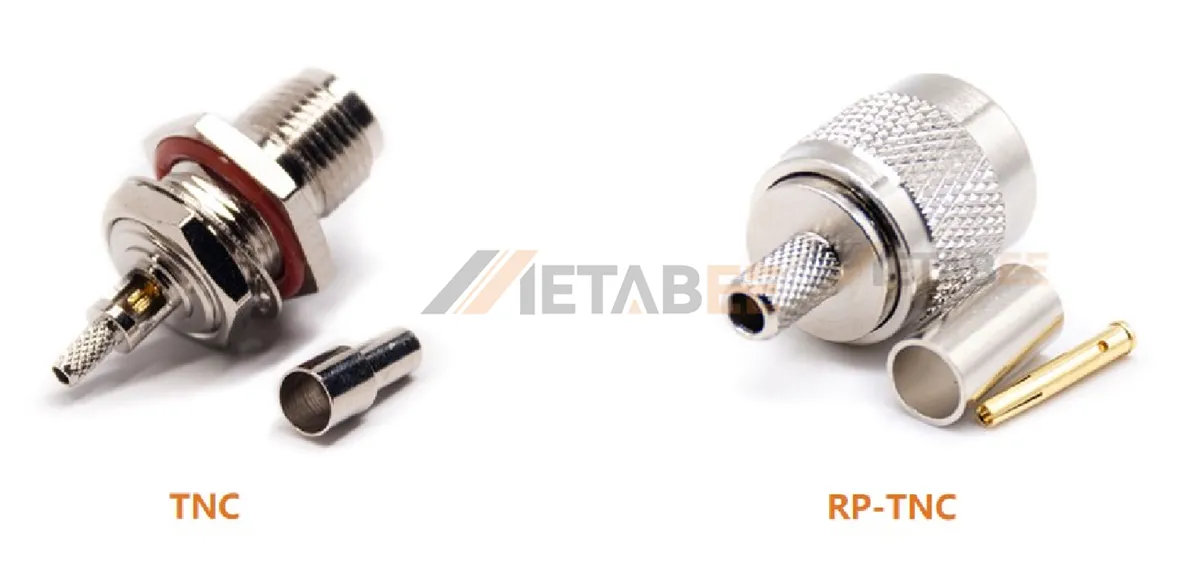
TNC vs RP-TNC Connectors
The TNC connector has two varieties–standard polarity (TNC)and reverse polarity (RP-TNC).
Reverse Polarity is the biggest difference between TNC connectors and RP-TNC connectors. TNC connectors adhere to the standard polarity, while RP-TNC connectors have a reverse polarity. Reverse Polarity TNC connectors have opposite genders of the center contact; the male connector has a receptacle while the female connector has a pin. So RP-TNC connectors are used in specific applications where reverse polarity is required.
There are the key differences between TNC and RP-TNC connectors:
| Feature | TNC Connector | RP-TNC Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Threaded Neill–Concelman | Reverse Polarity Threaded Neill–Concelman n |
| Polarity | Standard | Reverse Polarity |
| Male Connector | The threading is on the inside The center part is a pin | The threading is on the outside The center part is a hole |
| Female Connector | The threading is on the outside The center part is a hole | The threading is on the outside The center part is a pin |
| Available | Easily available | Not readily available |
| Price | Affordable | More expensive |
The main similarities of the two connectors are as follows:
| Feature | TNC Connector | RP-TNC Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Connector | Coaxial RF connector | |
| Mounting | Available in cable-type, panel-mount, pcb-mount versions | |
| Fastening Type | Threaded coupling | |
| Impedance | 50 Ohm | |
| Frequency Range | Typically DC to 6 GHz | |
| Main Materials | Body brass with nickel-plated Contact brass with gold-plated TEFLON insulator | |

How to Choose the Right TNC Connectors?
When choosing TNC connectors, it’s important to consider several factors to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. Here are some key points:
Frequency Range
You should consider the application’s operational frequency. TNC connectors are intended for high-frequency transmissions; however, the precise range must meet the individual product requirements.
Environmental Conditions
Considering the environmental conditions that connections will withstand, specifically severe temperatures, humidity, and vibration.
Connector Type
Selecting the suitable tnc connector type (male connector, female connector, right-angle connector, Panel Mount connector) based on application requirements and the practical devices you need to connect.
Pricing and Availability
You need to compare prices from different suppliers and find the best deal. While also considering other aspects such as shipping cost, minimum purchase quantities, and delivery periods.
Certifications and Standards
TNC coaxial connectors that you want to buy should meet appropriate industry standards and certifications.
The Main TNC Connector Manufacturers
Choosing a trustworthy manufacturer is paramount because it ensures consistent product quality, timely delivery, and exceptional customer support when purchasing TNC connectors.
Here are some top TNC manufacturers:
Amphenol. A globally recognized supplier of RF and microwave connectors.
TE Connectivity. There are broad combination series of TNC connectors.
Radiall. A well-established global manufacturer of interconnect solutions, and they offer a wide range of TNC connectors for various applications.
Metabee. Metabee is a famous manufacturer in the RF coaxial connector market, recognized for its exceptional quality, outstanding reliability, superior service, and full compliance with industry standards.
Renhotec. Renhotec is a leading manufacturer of high-quality coaxial interconnect products. They provide a comprehensive range of standard and custom connectors With a deep understanding of the RF field.
TNC Adapters and Cable Assemblies
Except for TNC connectors, Metabee also provides a comprehensive range of TNC adapters and TNC cable assemblies. Thus, it can provide a complete solution for your connectivity requirements.

Conclusion
TNC coaxial connectors fit diverse RF applications and are widely used in various industries. Their reliable and versatile type can provide secure connections, high-frequency performance, and durability.
This post provides an understanding of the types of TNC connectors, their specifications, and their application and comparison with other RF connectors. Consequently, you will have a complete knowledge module when selecting and using TNC connectors.
Related Products
- TNC Connectors
- SMA Connectors
- BNC Connectors
- SMA Adapters
- BNC Adapters
- SMA Cable Assemblies
- BNC Cable Assemblies